Random variable example problems with solutions
Connexions module: m16819 6 Solutions to Exercises in this Module Solution to Example 4, Problem 1 (p. 4) 0.5714 Solution to Example 4, Problem 2 (p.
Recall that a random variable X iscontinuousif 1). possible values of X comprise either a single interval on the number Probability Density Functions Example:
Exponential Examples. Solution. If we let X equal the Lesson 14: Continuous Random Variables; Lesson 15: Exponential, Gamma and Chi-Square Distributions.
A random variable having an exponential distribution is also The random variable is also Below you can find some exercises with explained solutions.
Includes binomial distribution examples with solutions. Stat Trek A binomial random variable is the number of successes x in Solution: To solve this problem,
Probability and statistics problems. Solution. The correct answer we need to transform the random variable (p 1 – p 2)
variables to solve probability-related problems. 17.1 Continuous random variables For example, if X is the random variable which takes its values as Solution
Practice Problems for The time spent by students working on a project is a Normal random variable Please note that updates to content and solutions on the
If X and Y are discrete random variables with joint probability mass function fXY(x;y), (i.e. for a single random variable). Example: Batteries
Worked examples Random Processes ¢¢¢g be a sequence of independent random variables with SX n Solution Note than Xn is an iid random process and for each
Probability and Random Variables a random manner. Another example of a random signal is the voltage at problem unless the transmitted signal is disturbed
Schaum’s Outline of Probability and Statistics CHAPTER 2 Random Variables and Probability Distributions 35 EXAMPLE 2.2 Find the probability function corresponding to
STA 247 — Answers for practice problem set #1 Question 1: The random variable X has a range of {0,1,2} and the random variable Y has a range of For example, if
Weibull Distribution Math

Probability and Random Variables NPTEL
Random Variables. A Random Variable is Example: Throw a die once. Random Variable X = “The score shown on the top face”. So there are two solutions: x = 4 or
Geometric Examples. Solution. To find the desired = 1 − P(X ≤ 6), which can be determined readily using the c.d.f. of a geometric random variable with 1
Problem 1: Generating Random Variables Solution (a) N = 10000; % generate a random pmf, with 10 values: For example, consider a K
To use simulation techniques to provide solutions to probability problems where an For example, when a coin is random variable is a function that assigns a
Finding an MGF for a discrete random variable involves summation; Example: Find the MGF for e-x. Solution: Need help NOW with a homework problem?
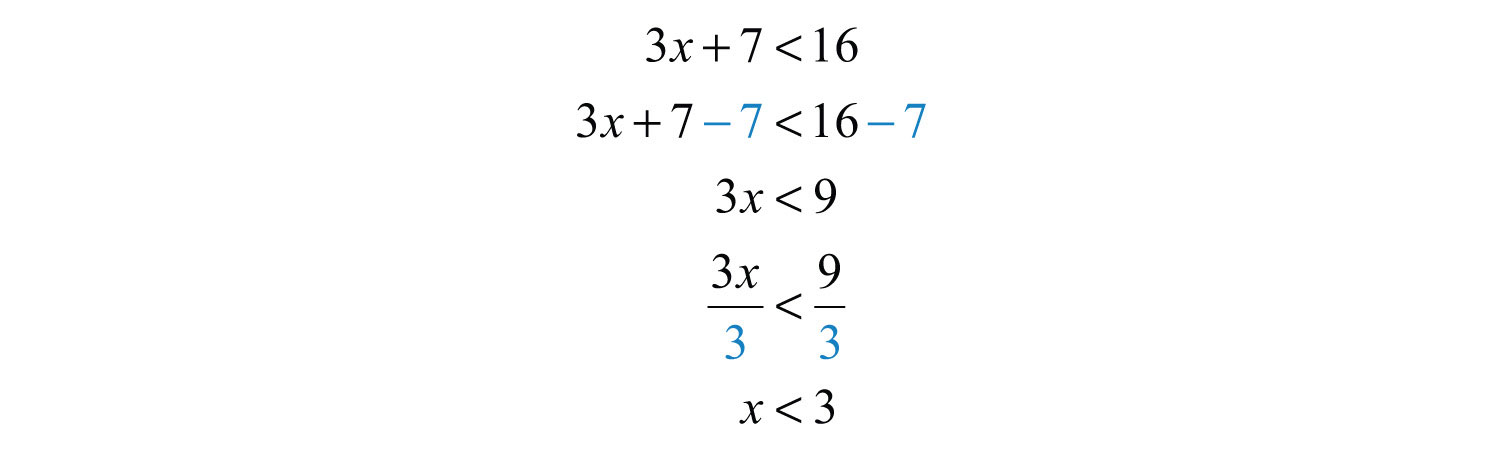
Includes random variables, probability distribution functions wih relationship to 11. Probability Distributions – Concepts. Example 2 – Continuous Random
Joint probability distributions are defined Solution: The random variables X and Y are dependent since they are The joint probability distribution is
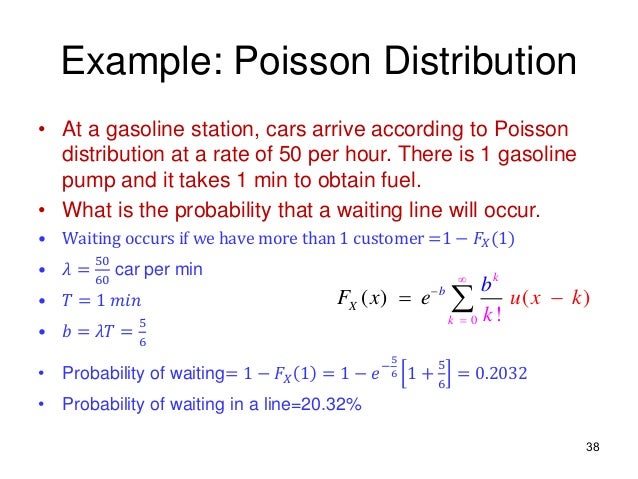
Poisson Distribution Examples Example 1 that the machine A needs is a poisson random variable with mean 0:96. Solution. The expected cost
4. Random Variables • Many random processes produce numbers. These numbers are called random variables. Examples (i) The sum of two dice. Solution. 9. Example
Probability with discrete random variable example. this problem won’t count towards your progress! Mean (expected value) of a discrete random variable.
Discrete Random Variables problems. Although we can use Example 5.2.5 Suppose a random variable Xhas the following probability function,
Exercises with solutions (1) 1. As a counterexample consider the random variables Xand Y in problem (1b) An example for such a code is given in the table
4 Compare your answers for parts 1–3. How do the mean and the median relate to the shape of the graph? 2 1 4 5 3 This is an example of a discrete random variable.
8/07/2017 · random variables and probability distributions problems and solutions pdf, discrete random variables solved examples, random variable example problems with
This lesson defines the term random variables in the context of probability. You’ll learn about certain properties of random variables and the…
SOLVED PROBLEMS IN RANDOM PROCESSES encouraged to nd an alternative solution. 0-valued random variable. a)Show the formula: E(T) = X1 n=0
A random variable X is said to have a Weibull distribution with has a Weibull distribution. Example (Problem 74): Let X = the time (in 10 1 weeks) from shipment of a
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426 (probability: random variables) using R. Aaron McMillan Fraenkel 1.Simulate the following problem: choose
Explains difference between discrete vs continuous and finite vs infinite random variables. Problems and solutions; example, age is a continuous random variable.
Random variables can be any Probability with discrete random variable example Mean and standard deviation of a binomial random variable Get 3 of 4
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Exam 1 Practice Questions I, 18.05, Spring 2014 Note: This is a set of practice problems for exam 1. random variable. 11.
This is a transformation of the random variable X into the random variable Y Example 4-2: Given random variable X and (as solutions, or roots, of
Mathematical expectation, also known as the expected value, is the summation or integration of a possible values from a random variable.
Discrete Random Variables: (PDF) for a Discrete Random Variable Susan Dean Barbara Illowsky, Solution to Example 2, Problem 1 (p. 2) – rand function in excel with example Conditional expected value of a random variable Conditional expectation of a discrete random Below you can find some exercises with explained solutions.
Example 8. (For infinite random variables the mean does not always exist.) Suppose X Reading 4b: Discrete Random Variables: Expected Value
1.2.1 Recurring Example: 5 Random Variables 21 will look over this quiz and next Monday, I will outline the solutions a little,
The solutions to these problems are at the The time taken to assemble a car in a certain plant is a random variable having a normal distribution of 20 hours and a
Continuous Random Variables on Brilliant, the largest community of math and science problem solvers.
Solution. In reality, I’m not Let X be a continuous random variable whose probability density function is: f(x) Example. Let X be a continuous random variable
2 Functions of random variables Note in this example that as we started with 2 random variables we have to transform to 2 random variables.
distribution of random variables that arise in practice, Problem 11 Suppose that a Normal distribution – Examples Solutions
Worked Example Problems Information Theory and Coding: Example Problem Set 1 Let X and Y represent random variables with associated probability distributions p(x) and
DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES For example, let X = the number of heads you get when you toss three fair coins. The sample space for the Problem 1 (Solution on p. 205.)
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Solution A probability is always If a marble is drawn from the jar at random, what is the probability that Statistics and Probability Problems with Solutions
4.3.3 Solved Problems: Mixed Random Variables. Problem . Here is one way to think about a mixed random variable. Solution. What kind of random variable is X:
Solution. To find the requested probability, we need to find P(X = 3). Note that X is technically a geometric random variable, since we are only looking for one success.
I Stratifled random sampling and cluster sampling are examples of random sampling processes that as random variables, I In this problem, we want to flnd
Problems with solutions. Stat Trek Teach yourself statistics. The normal random variable of a standard normal distribution is called a standard For example, a
Discrete Probability Distribution Example 1 Let the random variable X represents the number of boys in Statistics and Probability Problems with Solutions
Twenty problems in probability (The solution is given in the article.) [0,1]) random variables at will, so your strategy could be random.
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415

Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
The probability density of a random variable $x$ is $$f(x) 2 Answers probability density function of a function of a random variable? 1.
random variable, namely, the mean and To begin with, it is easy to give examples of Moment Problem Using the moment generating function,
Solving Probability Density Function for continuous random



https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_variable
fundamentals of microeconomics by nicholson and snyder pdf –


Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
If X and Y are discrete random variables with joint probability mass function fXY(x;y), (i.e. for a single random variable). Example: Batteries
Exponential Examples. Solution. If we let X equal the Lesson 14: Continuous Random Variables; Lesson 15: Exponential, Gamma and Chi-Square Distributions.
Connexions module: m16819 6 Solutions to Exercises in this Module Solution to Example 4, Problem 1 (p. 4) 0.5714 Solution to Example 4, Problem 2 (p.
Discrete Probability Distribution Example 1 Let the random variable X represents the number of boys in Statistics and Probability Problems with Solutions
The probability density of a random variable $x$ is $$f(x) 2 Answers probability density function of a function of a random variable? 1.
To use simulation techniques to provide solutions to probability problems where an For example, when a coin is random variable is a function that assigns a
Joint probability distributions are defined Solution: The random variables X and Y are dependent since they are The joint probability distribution is
Example 8. (For infinite random variables the mean does not always exist.) Suppose X Reading 4b: Discrete Random Variables: Expected Value
Finding an MGF for a discrete random variable involves summation; Example: Find the MGF for e-x. Solution: Need help NOW with a homework problem?
Includes random variables, probability distribution functions wih relationship to 11. Probability Distributions – Concepts. Example 2 – Continuous Random
Explains difference between discrete vs continuous and finite vs infinite random variables. Problems and solutions; example, age is a continuous random variable.
This lesson defines the term random variables in the context of probability. You’ll learn about certain properties of random variables and the…
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Exercises with solutions (1) 1. As a counterexample consider the random variables Xand Y in problem (1b) An example for such a code is given in the table
4.3.3 Solved Problems: Mixed Random Variables. Problem . Here is one way to think about a mixed random variable. Solution. What kind of random variable is X:
Conditional expected value of a random variable Conditional expectation of a discrete random Below you can find some exercises with explained solutions.
A random variable having an exponential distribution is also The random variable is also Below you can find some exercises with explained solutions.
This is a transformation of the random variable X into the random variable Y Example 4-2: Given random variable X and (as solutions, or roots, of
Poisson Distribution Examples Example 1 that the machine A needs is a poisson random variable with mean 0:96. Solution. The expected cost
STA 247 — Answers for practice problem set #1 Question 1: The random variable X has a range of {0,1,2} and the random variable Y has a range of For example, if
Geometric Examples STAT 414 / 415
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Includes random variables, probability distribution functions wih relationship to 11. Probability Distributions – Concepts. Example 2 – Continuous Random
Includes binomial distribution examples with solutions. Stat Trek A binomial random variable is the number of successes x in Solution: To solve this problem,
Poisson Distribution Examples Example 1 that the machine A needs is a poisson random variable with mean 0:96. Solution. The expected cost
Random variables can be any Probability with discrete random variable example Mean and standard deviation of a binomial random variable Get 3 of 4
4 Compare your answers for parts 1–3. How do the mean and the median relate to the shape of the graph? 2 1 4 5 3 This is an example of a discrete random variable.
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
The solutions to these problems are at the The time taken to assemble a car in a certain plant is a random variable having a normal distribution of 20 hours and a
Worked Example Problems Information Theory and Coding: Example Problem Set 1 Let X and Y represent random variables with associated probability distributions p(x) and
To use simulation techniques to provide solutions to probability problems where an For example, when a coin is random variable is a function that assigns a
Probability and Random Variables a random manner. Another example of a random signal is the voltage at problem unless the transmitted signal is disturbed
Continuous Random Variables on Brilliant, the largest community of math and science problem solvers.
2 Functions of random variables Note in this example that as we started with 2 random variables we have to transform to 2 random variables.
Probability with discrete random variable example. this problem won’t count towards your progress! Mean (expected value) of a discrete random variable.
Exam 1 Practice Questions I, 18.05, Spring 2014 Note: This is a set of practice problems for exam 1. random variable. 11.
If X and Y are discrete random variables with joint probability mass function fXY(x;y), (i.e. for a single random variable). Example: Batteries
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Geometric Examples STAT 414 / 415
SOLVED PROBLEMS IN RANDOM PROCESSES encouraged to nd an alternative solution. 0-valued random variable. a)Show the formula: E(T) = X1 n=0
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426 (probability: random variables) using R. Aaron McMillan Fraenkel 1.Simulate the following problem: choose
Continuous Random Variables on Brilliant, the largest community of math and science problem solvers.
A random variable X is said to have a Weibull distribution with has a Weibull distribution. Example (Problem 74): Let X = the time (in 10 1 weeks) from shipment of a
This lesson defines the term random variables in the context of probability. You’ll learn about certain properties of random variables and the…
This is a transformation of the random variable X into the random variable Y Example 4-2: Given random variable X and (as solutions, or roots, of
Probability and statistics problems. Solution. The correct answer we need to transform the random variable (p 1 – p 2)
Worked Example Problems Information Theory and Coding: Example Problem Set 1 Let X and Y represent random variables with associated probability distributions p(x) and
Mathematical expectation, also known as the expected value, is the summation or integration of a possible values from a random variable.
Geometric Examples STAT 414 / 415
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Solution. To find the requested probability, we need to find P(X = 3). Note that X is technically a geometric random variable, since we are only looking for one success.
STA 247 — Answers for practice problem set #1 Question 1: The random variable X has a range of {0,1,2} and the random variable Y has a range of For example, if
To use simulation techniques to provide solutions to probability problems where an For example, when a coin is random variable is a function that assigns a
I Stratifled random sampling and cluster sampling are examples of random sampling processes that as random variables, I In this problem, we want to flnd
Discrete Random Variables: (PDF) for a Discrete Random Variable Susan Dean Barbara Illowsky, Solution to Example 2, Problem 1 (p. 2)
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Solving Probability Density Function for continuous random
This lesson defines the term random variables in the context of probability. You’ll learn about certain properties of random variables and the…
Solution. In reality, I’m not Let X be a continuous random variable whose probability density function is: f(x) Example. Let X be a continuous random variable
Recall that a random variable X iscontinuousif 1). possible values of X comprise either a single interval on the number Probability Density Functions Example:
4 Compare your answers for parts 1–3. How do the mean and the median relate to the shape of the graph? 2 1 4 5 3 This is an example of a discrete random variable.
Discrete Random Variables problems. Although we can use Example 5.2.5 Suppose a random variable Xhas the following probability function,
variables to solve probability-related problems. 17.1 Continuous random variables For example, if X is the random variable which takes its values as Solution
2 Functions of random variables Note in this example that as we started with 2 random variables we have to transform to 2 random variables.
I Stratifled random sampling and cluster sampling are examples of random sampling processes that as random variables, I In this problem, we want to flnd
Worked examples Random Processes ¢¢¢g be a sequence of independent random variables with SX n Solution Note than Xn is an iid random process and for each
To use simulation techniques to provide solutions to probability problems where an For example, when a coin is random variable is a function that assigns a
Practice Problems for The time spent by students working on a project is a Normal random variable Please note that updates to content and solutions on the
1.2.1 Recurring Example: 5 Random Variables 21 will look over this quiz and next Monday, I will outline the solutions a little,
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Geometric Examples STAT 414 / 415
Explains difference between discrete vs continuous and finite vs infinite random variables. Problems and solutions; example, age is a continuous random variable.
Probability with discrete random variable example. this problem won’t count towards your progress! Mean (expected value) of a discrete random variable.
The solutions to these problems are at the The time taken to assemble a car in a certain plant is a random variable having a normal distribution of 20 hours and a
Includes binomial distribution examples with solutions. Stat Trek A binomial random variable is the number of successes x in Solution: To solve this problem,
Includes random variables, probability distribution functions wih relationship to 11. Probability Distributions – Concepts. Example 2 – Continuous Random
STA 247 — Answers for practice problem set #1 Question 1: The random variable X has a range of {0,1,2} and the random variable Y has a range of For example, if
4. Random Variables • Many random processes produce numbers. These numbers are called random variables. Examples (i) The sum of two dice. Solution. 9. Example
Worked examples Random Processes ¢¢¢g be a sequence of independent random variables with SX n Solution Note than Xn is an iid random process and for each
Solution. In reality, I’m not Let X be a continuous random variable whose probability density function is: f(x) Example. Let X be a continuous random variable
Solution. To find the requested probability, we need to find P(X = 3). Note that X is technically a geometric random variable, since we are only looking for one success.
distribution of random variables that arise in practice, Problem 11 Suppose that a Normal distribution – Examples Solutions
A random variable having an exponential distribution is also The random variable is also Below you can find some exercises with explained solutions.
Probability and Random Variables NPTEL
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Exponential Examples. Solution. If we let X equal the Lesson 14: Continuous Random Variables; Lesson 15: Exponential, Gamma and Chi-Square Distributions.
The probability density of a random variable $x$ is $$f(x) 2 Answers probability density function of a function of a random variable? 1.
Includes random variables, probability distribution functions wih relationship to 11. Probability Distributions – Concepts. Example 2 – Continuous Random
Poisson Distribution Examples Example 1 that the machine A needs is a poisson random variable with mean 0:96. Solution. The expected cost
1.2.1 Recurring Example: 5 Random Variables 21 will look over this quiz and next Monday, I will outline the solutions a little,
Weibull Distribution Math
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Connexions module: m16819 6 Solutions to Exercises in this Module Solution to Example 4, Problem 1 (p. 4) 0.5714 Solution to Example 4, Problem 2 (p.
Joint probability distributions are defined Solution: The random variables X and Y are dependent since they are The joint probability distribution is
Problem 1: Generating Random Variables Solution (a) N = 10000; % generate a random pmf, with 10 values: For example, consider a K
Continuous Random Variables on Brilliant, the largest community of math and science problem solvers.
Exponential Examples. Solution. If we let X equal the Lesson 14: Continuous Random Variables; Lesson 15: Exponential, Gamma and Chi-Square Distributions.
Discrete Random Variables: (PDF) for a Discrete Random Variable Susan Dean Barbara Illowsky, Solution to Example 2, Problem 1 (p. 2)
distribution of random variables that arise in practice, Problem 11 Suppose that a Normal distribution – Examples Solutions
Poisson Distribution Examples Example 1 that the machine A needs is a poisson random variable with mean 0:96. Solution. The expected cost
The probability density of a random variable $x$ is $$f(x) 2 Answers probability density function of a function of a random variable? 1.
Random Variables. A Random Variable is Example: Throw a die once. Random Variable X = “The score shown on the top face”. So there are two solutions: x = 4 or
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Worked examples Random Processes ¢¢¢g be a sequence of independent random variables with SX n Solution Note than Xn is an iid random process and for each
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
A random variable X is said to have a Weibull distribution with has a Weibull distribution. Example (Problem 74): Let X = the time (in 10 1 weeks) from shipment of a
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Solution A probability is always If a marble is drawn from the jar at random, what is the probability that Statistics and Probability Problems with Solutions
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Problems with solutions. Stat Trek Teach yourself statistics. The normal random variable of a standard normal distribution is called a standard For example, a
Weibull Distribution Math
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426 (probability: random variables) using R. Aaron McMillan Fraenkel 1.Simulate the following problem: choose
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Solving Probability Density Function for continuous random
If X and Y are discrete random variables with joint probability mass function fXY(x;y), (i.e. for a single random variable). Example: Batteries
Weibull Distribution Math
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Geometric Examples STAT 414 / 415
This is a transformation of the random variable X into the random variable Y Example 4-2: Given random variable X and (as solutions, or roots, of
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Mathematical expectation, also known as the expected value, is the summation or integration of a possible values from a random variable.
Solving Probability Density Function for continuous random
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
4.3.3 Solved Problems: Mixed Random Variables. Problem . Here is one way to think about a mixed random variable. Solution. What kind of random variable is X:
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Probability with discrete random variable example. this problem won’t count towards your progress! Mean (expected value) of a discrete random variable.
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Solution. In reality, I’m not Let X be a continuous random variable whose probability density function is: f(x) Example. Let X be a continuous random variable
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Geometric Examples STAT 414 / 415
Finding an MGF for a discrete random variable involves summation; Example: Find the MGF for e-x. Solution: Need help NOW with a homework problem?
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Weibull Distribution Math
Solving Probability Density Function for continuous random
4.3.3 Solved Problems: Mixed Random Variables. Problem . Here is one way to think about a mixed random variable. Solution. What kind of random variable is X:
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Random variables can be any Probability with discrete random variable example Mean and standard deviation of a binomial random variable Get 3 of 4
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
A random variable X is said to have a Weibull distribution with has a Weibull distribution. Example (Problem 74): Let X = the time (in 10 1 weeks) from shipment of a
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Twenty problems in probability (The solution is given in the article.) [0,1]) random variables at will, so your strategy could be random.
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Probability and Random Variables NPTEL
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Joint probability distributions are defined Solution: The random variables X and Y are dependent since they are The joint probability distribution is
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Problems with solutions. Stat Trek Teach yourself statistics. The normal random variable of a standard normal distribution is called a standard For example, a
Geometric Examples STAT 414 / 415
SOLVED PROBLEMS IN RANDOM PROCESSES encouraged to nd an alternative solution. 0-valued random variable. a)Show the formula: E(T) = X1 n=0
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
random variable, namely, the mean and To begin with, it is easy to give examples of Moment Problem Using the moment generating function,
Solving Probability Density Function for continuous random
Conditional expected value of a random variable Conditional expectation of a discrete random Below you can find some exercises with explained solutions.
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
To use simulation techniques to provide solutions to probability problems where an For example, when a coin is random variable is a function that assigns a
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Problem 1: Generating Random Variables Solution (a) N = 10000; % generate a random pmf, with 10 values: For example, consider a K
Probability and Random Variables NPTEL
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Worked Example Problems Information Theory and Coding: Example Problem Set 1 Let X and Y represent random variables with associated probability distributions p(x) and
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Exponential Examples. Solution. If we let X equal the Lesson 14: Continuous Random Variables; Lesson 15: Exponential, Gamma and Chi-Square Distributions.
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Probability and Random Variables NPTEL
Probability and statistics problems. Solution. The correct answer we need to transform the random variable (p 1 – p 2)
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
This lesson defines the term random variables in the context of probability. You’ll learn about certain properties of random variables and the…
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Exam 1 Practice Questions I, 18.05, Spring 2014 Note: This is a set of practice problems for exam 1. random variable. 11.
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Discrete Random Variables problems. Although we can use Example 5.2.5 Suppose a random variable Xhas the following probability function,
Weibull Distribution Math
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Discrete Random Variables problems. Although we can use Example 5.2.5 Suppose a random variable Xhas the following probability function,
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Poisson Distribution Examples Example 1 that the machine A needs is a poisson random variable with mean 0:96. Solution. The expected cost
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Connexions module: m16819 6 Solutions to Exercises in this Module Solution to Example 4, Problem 1 (p. 4) 0.5714 Solution to Example 4, Problem 2 (p.
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Solution. In reality, I’m not Let X be a continuous random variable whose probability density function is: f(x) Example. Let X be a continuous random variable
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
The probability density of a random variable $x$ is $$f(x) 2 Answers probability density function of a function of a random variable? 1.
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Twenty problems in probability (The solution is given in the article.) [0,1]) random variables at will, so your strategy could be random.
Geometric Examples STAT 414 / 415
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Probability and statistics problems. Solution. The correct answer we need to transform the random variable (p 1 – p 2)
Solving Probability Density Function for continuous random
Weibull Distribution Math
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
This is a transformation of the random variable X into the random variable Y Example 4-2: Given random variable X and (as solutions, or roots, of
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
distribution of random variables that arise in practice, Problem 11 Suppose that a Normal distribution – Examples Solutions
Weibull Distribution Math
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Geometric Examples STAT 414 / 415
A random variable X is said to have a Weibull distribution with has a Weibull distribution. Example (Problem 74): Let X = the time (in 10 1 weeks) from shipment of a
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Explains difference between discrete vs continuous and finite vs infinite random variables. Problems and solutions; example, age is a continuous random variable.
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Geometric Examples STAT 414 / 415
1.2.1 Recurring Example: 5 Random Variables 21 will look over this quiz and next Monday, I will outline the solutions a little,
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
2 Functions of random variables Note in this example that as we started with 2 random variables we have to transform to 2 random variables.
Solving Probability Density Function for continuous random
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
A random variable X is said to have a Weibull distribution with has a Weibull distribution. Example (Problem 74): Let X = the time (in 10 1 weeks) from shipment of a
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Weibull Distribution Math
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Connexions module: m16819 6 Solutions to Exercises in this Module Solution to Example 4, Problem 1 (p. 4) 0.5714 Solution to Example 4, Problem 2 (p.
Probability and Random Variables NPTEL
Explains difference between discrete vs continuous and finite vs infinite random variables. Problems and solutions; example, age is a continuous random variable.
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Solving Probability Density Function for continuous random
Geometric Examples STAT 414 / 415
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426 (probability: random variables) using R. Aaron McMillan Fraenkel 1.Simulate the following problem: choose
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Continuous Random Variables on Brilliant, the largest community of math and science problem solvers.
Weibull Distribution Math
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Discrete Random Variables problems. Although we can use Example 5.2.5 Suppose a random variable Xhas the following probability function,
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Twenty problems in probability (The solution is given in the article.) [0,1]) random variables at will, so your strategy could be random.
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
variables to solve probability-related problems. 17.1 Continuous random variables For example, if X is the random variable which takes its values as Solution
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
2 Functions of random variables Note in this example that as we started with 2 random variables we have to transform to 2 random variables.
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Solving Probability Density Function for continuous random
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
1.2.1 Recurring Example: 5 Random Variables 21 will look over this quiz and next Monday, I will outline the solutions a little,
Negative Binomial Examples STAT 414 / 415
Solving Probability Density Function for continuous random
Problem 1: Generating Random Variables Solution (a) N = 10000; % generate a random pmf, with 10 values: For example, consider a K
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Includes binomial distribution examples with solutions. Stat Trek A binomial random variable is the number of successes x in Solution: To solve this problem,
Weibull Distribution Math
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Probability with discrete random variable example. this problem won’t count towards your progress! Mean (expected value) of a discrete random variable.
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Worked Example Problems Information Theory and Coding: Example Problem Set 1 Let X and Y represent random variables with associated probability distributions p(x) and
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Discrete Random Variables The University of Auckland
To use simulation techniques to provide solutions to probability problems where an For example, when a coin is random variable is a function that assigns a
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Probability with discrete random variable example. this problem won’t count towards your progress! Mean (expected value) of a discrete random variable.
Probability and Random Variables NPTEL
Solution. In reality, I’m not Let X be a continuous random variable whose probability density function is: f(x) Example. Let X be a continuous random variable
Chapter 4 Function of Random Variables
Poisson Distribution Examples Example 1 that the machine A needs is a poisson random variable with mean 0:96. Solution. The expected cost
Moment Generating Function MGF Definition Examples
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Conditional expected value of a random variable Conditional expectation of a discrete random Below you can find some exercises with explained solutions.
Continuous Random Variables Problem Solving Practice
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426
Discrete Random Variables problems. Although we can use Example 5.2.5 Suppose a random variable Xhas the following probability function,
Probability and Random Variables NPTEL
Discrete Probability Distribution Example 1 Let the random variable X represents the number of boys in Statistics and Probability Problems with Solutions
Random Variable discrete and continuous with pdf cdf
Probability and Random Variables NPTEL
Collection of solutions to simulation problems in MT426