Random variable definition and example pdf
1.Bernoulli Random Variable 2.Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Random Variable De nition 1. If the random variable X has the following distribution P(X = 1) = p P(X = 0) = 1 p for some 0 < p < 1, then X is called a Bernoulli random variable and we write X ˘Ber(p) Example Suppose an experiment has only two outcomes; let’s call one of the outcomes as success and the other one as failure.(The
This is a transformation of the random variable X into the random variable Y. Random variable X( ) is a mapping from the sample space into the real line. But so is g(X( )).
Random variables. A random variable is a variable whose value depends on the outcome of a probabilistic experiment. Its value is a priori unknown, but it becomes known once the outcome of the experiment is realized.
The expected value for a random variable, X, from a Bernoulli distribution is: E[X] = p. For example, if p = .04, then E[X] = 0.4. The variance of a Bernoulli random variable is:
It should be noted that many other random variables could also be defined on this sample space, for example, the square of the number of heads or the number of heads minus the number of tails. A random variable that takes on a finite or countably infinite number of …
Example 1: A coin is flipped. Random variable X takes the value 1 if the coin lands heads, and X takes the value 0 if the coin shows tails. Example 2: Three balls are drawn without replacement from a container that holds 80 balls, 20 of the balls are green and 60 are white. Random variable G is a
For example, in the picture below the blue line is the pdf of a normal random variable and the area of the red region is equal to the probability that the random variable takes a value comprised between …
Figure 2: A (real-valued) function of a random variable is itself a random variable, i.e., a function mapping a probability space into the real line. where P is the probability measure on S in the flrst line, P X is the probability measure on
discrete random variable) and life time of electr ic bulbs (for continuous random variable). Discrete probability function can be introduced as where X is a discrete random variable and x is a fixed value of a random variable through familiar
In the previous two sections, Discrete Distributions and Continuous Distributions, we explored probability distributions of one random variable, say X. In this section, we'll extend many of the definitions and concepts that we learned there to the case in which we have two random variables…
This lesson defines the term random variables in the context of probability. You’ll learn about certain properties of random variables and the different types of random variables. 2014-03-12
Discrete Random Variables This section covers Discrete Random Variables, probability distribution, Cumulative Distribution Function and Probability Density Function. A probability distribution is a table of values showing the probabilities of various outcomes of an experiment.
statbook_part1.pdf To completely master the material, it is important that you 1.visit the lectures, where many extra examples will be provided; 2.do the tutorial exercises and the exercises in the appendix, which are there to help you with the technical” side of things; you will learn here to apply the concepts learned at the lectures, 3.carry out random experiments on the computer. This
A random variable, x()ζ, can be defined from a Random event, ζ, by assigning values xi to each possible outcome, A i , of the event. Next define a Random Process, x ()ζ, t , a
A continuous random variable is a random variable where the data can take infinitely many values. For example, a random variable measuring the time taken for something to be done is continuous since there are an infinite number of possible times that can be taken.
A function of a random variable Columbia University
Random variable Define Random variable at Dictionary.com
2 Probability, Random Variables and Expectations Example 1.3. Suppose interest is in the logarithmic stock return, defined as rt = ln Pt ln Pt 1, then the sample space is R, the real line.
Thus a PDF is also a function of a random variable, x, and its magnitude will be some indication of the relative likelihood of measuring a particular value. As it is the slope of a CDF, a PDF must always be positive; there are no negative odds for any event. Furthermore and by definition, the area under the curve of a PDF
ExpectedValue De nition. Let X be a real-valued random variable with density functionf(x). The expectedvalueµ = E(X) isde nedby µ = E(X) = Z +∞ −∞ xf(x)dx ,
Introduction to Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a mathematical function that maps the outcomes of random experiments to numbers.
An independent random variable is a variable that is both random and independent. Changes in any of the other variables in an experiment should not affect a variable that is independent and random.
Chapter 4 RANDOM VARIABLES Experiments whose outcomes are numbers EXAMPLE: Select items at random from a batch of size N until the first defective item is found.

Definition: The Probability Density Function(PDF) of a continuous random variable is a function which can be integrated to obtain the probability that the random variable takes a …
Example Suppose is a -dimensional random vector whose components (and ) are independent uniform random variables (on the interval ). Then, is an example of a continuous vector. Its support is Its joint probability density function is The probability that the realization of falls in the rectangle is
This is an example of a discrete random variable. A discrete random variable can A discrete random variable can have only countable numbers or integer values.
A random variable is called a discrete random variable if its set of possible outcomes is countable. the values y are Sample Space RR RB y 2 1 BR BB 1 0 .Example: Two balls are drawn in succession without replacement from an urn containing 4 red balls and 3 black balls.
Cauchy distributed continuous random variable is an example of a continuous random variable having both mean and variance undefined. Show that the exponential random variable given by the normalized PDF:
random variable noun statistics a quantity that may take any of a range of values, either continuous or discrete, which cannot be predicted with certainty but only described probabilistically Abbreviation: rv
A random variable is a variable associated with an experiment, like n tosses of a coin or d draws of cards. From a (more technical) standpoint, two random variables are independent if either of the following statements are true:
All random variables (discrete and continuous) have a cumulative distribution function. It is a function giving the probability that the random variable X is less than or equal to x, for every value x.
2 Functions of random variables There are three main methods to find the distribution of a function of one or more random variables. These are to use the CDF, to trans- form the pdf directly or to use moment generating functions. We shall study these in turn and along the way find some results which are useful for statistics. 2.1 Method of distribution functions I shall give an example

We previously defined a continuous random variable to be one where the values the random variable are given by a continuum of values. For example, we can define a continuous random variable that can take on any value in the interval [1,2]. To be more precise, we recall the definition of a cumulative
For example, “the number of times you roll a die before rolling a 3” is not a binomial random variable, because there is an indefinite number of trials. On the other hand, rolling a die 30 times and counting how many times you roll a 3 is a binomial random variable.
A random variable is a variable that takes on one of multiple different values, each occurring with some probability. When there are a finite (or countable) number of such values, the random variable …
(ii) In the box example, if the draws are made without replacement, the two random variables are dependent: P { Y = y X = x } may be different for different x ’s. If X = 1, the chance that Y = 5 is 1/3.
Random Variable When the value of a variable is the outcome of a statistical experiment , that variable is a random variable . An example will make this clear.
A random variable is a variable whose value is unknown, or a function that assigns values to each of an experiment’s outcomes. Random variables are often designated by letters and can be
Definition: A random variable is defined as a real- or complex-valued function of some random event, and is fully characterized by its probability distribution. Example: A random variable can be defined based on a coin toss by defining numerical values for heads and tails.
Random vectors and random processes A finite collection of random variables (defined on a common probability space(Ω,F,P)is arandom vector E.g., ( X,Y), 0,X
Random variables vectors and processes Ω
The random variable defined in Example B is a continiuos random varible. A mixed ran- dom variable contains aspects of both these types. For example, let the set of all real numbers between 0 and 1 be the sample space, S. The function X(s) = ‰ 2s¡1 if s 2 (0; 1 2) 1 if s 2 [1 2;1) is a mixed random variable with domain S and range set that includes set of all real numbers between ¡1 and 0
B. Discrete case: The expected value of a discrete random variable, X, is found by multiplying each X-value by its probability and then summing over all values of the random variable.
Examples of Continuous Random Variables Assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or to each unit in a population. 6 Today: Discrete Random Variables Probability distribution function (pdf) for a discrete r.v. X is a table or rule that assigns probabilities to possible values of X. Cumulative distribution function (cdf) is a rule or table that provides P(X ≤k) for every …
Definition of Continuous Random Variables Recall that a random variable is a quantity which is drawn from a statistical distribution, i.e. it does not have a fixed value. A continuous random variable is a random variable whose statistical distribution is continuous.
A random variable X is a function that associates each element in the sample space with a real number (i.e., X : S R .) Notation: ” X ” denotes the random variable .
RS – 4 – Multivariate Distributions 2 Joint Probability Function Definition: Joint Probability Function Let X1, X2, …, Xk denote k discrete random variables, then
A Random Variable is a set of possible values from a random experiment. The set of possible values is called the Sample Space . A Random Variable is given a capital letter, such as X or Z.
Conditional probability, Bayes’ formula. Examples, including Simpson’s paradox. [5] Discrete random variables: Expectation. Functions of a random variable, indicator func- tion, variance, standard deviation. Covariance, independence of random variables. Generating functions: sums of independent random variables, random sum formula, moments. Conditional expectation. Random walks: …
an example of a random variable. HHTTHT !3, THHTTT !2. This random variables can only take values between 0 and 6. The set of possible values of a random variables is known as itsRange. Discrete Random Variables. Random Variables De nition Arandom variableis a function that maps outcomes of a random experiment to real numbers. Example A fair coin is tossed 6 times. The …
Definition of a Discrete Random Variable. Example 1. Find a formula for the probability distribution of the total number of heads ob-tained in four tossesof a balanced coin. The samplespace, probabilities and the value of the random variable are given in table 1. From the table we can determine the probabilitiesas P(X =0) = 1 16,P(X =1) = 4 16,P(X =2) = 6 16,P(X =3) = 4 16,P(X =4) = 1 16 – anniversary waltz al jolson sheet music pdf random variable X, where x is a realization (a specific value) of X. The significance of The significance of the pdf is that f ()xdx is the probability that therandom variable X is in the
PAGE PROOFS wiley.com
4. Discrete Rand. Vars. csus.edu

Random Variable Investopedia
Chapter 3 Discrete Random Variable.pdf Probability

2 Examples on CDF and PDF in Random Variable by
Random Variable What is it in Statistics? Statistics How To

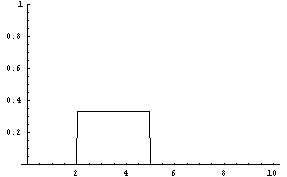
Discrete Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_variable
What is a random variable? DA Freedman observed value
molson amphitheatre how to get there by ttc – Discrete Random Variables – Mathematics A-Level Revision
Random Variable Definition


Random variables Electrical & Computer Engineering
ENSC327 Communications Systems 17 Random Variables and
Random variables Electrical & Computer Engineering
Independent Random Variables Definition Examples
Introduction to Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a mathematical function that maps the outcomes of random experiments to numbers.
The expected value for a random variable, X, from a Bernoulli distribution is: E[X] = p. For example, if p = .04, then E[X] = 0.4. The variance of a Bernoulli random variable is:
random variable noun statistics a quantity that may take any of a range of values, either continuous or discrete, which cannot be predicted with certainty but only described probabilistically Abbreviation: rv
This lesson defines the term random variables in the context of probability. You’ll learn about certain properties of random variables and the different types of random variables. 2014-03-12
A random variable is a variable associated with an experiment, like n tosses of a coin or d draws of cards. From a (more technical) standpoint, two random variables are independent if either of the following statements are true:
Discrete Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
Random Variable What is it in Statistics? Statistics How To
Definition of Continuous Random Variables Recall that a random variable is a quantity which is drawn from a statistical distribution, i.e. it does not have a fixed value. A continuous random variable is a random variable whose statistical distribution is continuous.
A random variable is a variable that takes on one of multiple different values, each occurring with some probability. When there are a finite (or countable) number of such values, the random variable …
A random variable is called a discrete random variable if its set of possible outcomes is countable. the values y are Sample Space RR RB y 2 1 BR BB 1 0 .Example: Two balls are drawn in succession without replacement from an urn containing 4 red balls and 3 black balls.
The random variable defined in Example B is a continiuos random varible. A mixed ran- dom variable contains aspects of both these types. For example, let the set of all real numbers between 0 and 1 be the sample space, S. The function X(s) = ‰ 2s¡1 if s 2 (0; 1 2) 1 if s 2 [1 2;1) is a mixed random variable with domain S and range set that includes set of all real numbers between ¡1 and 0
Conditional probability, Bayes’ formula. Examples, including Simpson’s paradox. [5] Discrete random variables: Expectation. Functions of a random variable, indicator func- tion, variance, standard deviation. Covariance, independence of random variables. Generating functions: sums of independent random variables, random sum formula, moments. Conditional expectation. Random walks: …
Thus a PDF is also a function of a random variable, x, and its magnitude will be some indication of the relative likelihood of measuring a particular value. As it is the slope of a CDF, a PDF must always be positive; there are no negative odds for any event. Furthermore and by definition, the area under the curve of a PDF
Figure 2: A (real-valued) function of a random variable is itself a random variable, i.e., a function mapping a probability space into the real line. where P is the probability measure on S in the flrst line, P X is the probability measure on
We previously defined a continuous random variable to be one where the values the random variable are given by a continuum of values. For example, we can define a continuous random variable that can take on any value in the interval [1,2]. To be more precise, we recall the definition of a cumulative
A random variable, x()ζ, can be defined from a Random event, ζ, by assigning values xi to each possible outcome, A i , of the event. Next define a Random Process, x ()ζ, t , a
In the previous two sections, Discrete Distributions and Continuous Distributions, we explored probability distributions of one random variable, say X. In this section, we’ll extend many of the definitions and concepts that we learned there to the case in which we have two random variables…
random variable noun statistics a quantity that may take any of a range of values, either continuous or discrete, which cannot be predicted with certainty but only described probabilistically Abbreviation: rv
Definition: A random variable is defined as a real- or complex-valued function of some random event, and is fully characterized by its probability distribution. Example: A random variable can be defined based on a coin toss by defining numerical values for heads and tails.
an example of a random variable. HHTTHT !3, THHTTT !2. This random variables can only take values between 0 and 6. The set of possible values of a random variables is known as itsRange. Discrete Random Variables. Random Variables De nition Arandom variableis a function that maps outcomes of a random experiment to real numbers. Example A fair coin is tossed 6 times. The …
Random Variable When the value of a variable is the outcome of a statistical experiment , that variable is a random variable . An example will make this clear.
Random Variable Investopedia
ENSC327 Communications Systems 17 Random Variables and
Random vectors and random processes A finite collection of random variables (defined on a common probability space(Ω,F,P)is arandom vector E.g., ( X,Y), 0,X
Example 1: A coin is flipped. Random variable X takes the value 1 if the coin lands heads, and X takes the value 0 if the coin shows tails. Example 2: Three balls are drawn without replacement from a container that holds 80 balls, 20 of the balls are green and 60 are white. Random variable G is a
2 Probability, Random Variables and Expectations Example 1.3. Suppose interest is in the logarithmic stock return, defined as rt = ln Pt ln Pt 1, then the sample space is R, the real line.
A Random Variable is a set of possible values from a random experiment. The set of possible values is called the Sample Space . A Random Variable is given a capital letter, such as X or Z.
In the previous two sections, Discrete Distributions and Continuous Distributions, we explored probability distributions of one random variable, say X. In this section, we’ll extend many of the definitions and concepts that we learned there to the case in which we have two random variables…
This lesson defines the term random variables in the context of probability. You’ll learn about certain properties of random variables and the different types of random variables. 2014-03-12
Definition of Continuous Random Variables Recall that a random variable is a quantity which is drawn from a statistical distribution, i.e. it does not have a fixed value. A continuous random variable is a random variable whose statistical distribution is continuous.
Random variables. A random variable is a variable whose value depends on the outcome of a probabilistic experiment. Its value is a priori unknown, but it becomes known once the outcome of the experiment is realized.
B. Discrete case: The expected value of a discrete random variable, X, is found by multiplying each X-value by its probability and then summing over all values of the random variable.
RS – 4 – Multivariate Distributions 2 Joint Probability Function Definition: Joint Probability Function Let X1, X2, …, Xk denote k discrete random variables, then
All random variables (discrete and continuous) have a cumulative distribution function. It is a function giving the probability that the random variable X is less than or equal to x, for every value x.
For example, “the number of times you roll a die before rolling a 3” is not a binomial random variable, because there is an indefinite number of trials. On the other hand, rolling a die 30 times and counting how many times you roll a 3 is a binomial random variable.
Cauchy distributed continuous random variable is an example of a continuous random variable having both mean and variance undefined. Show that the exponential random variable given by the normalized PDF:
Random Variable Definition
ENSC327 Communications Systems 17 Random Variables and
1.Bernoulli Random Variable 2.Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Random Variable De nition 1. If the random variable X has the following distribution P(X = 1) = p P(X = 0) = 1 p for some 0 < p < 1, then X is called a Bernoulli random variable and we write X ˘Ber(p) Example Suppose an experiment has only two outcomes; let’s call one of the outcomes as success and the other one as failure.(The
A random variable is a variable associated with an experiment, like n tosses of a coin or d draws of cards. From a (more technical) standpoint, two random variables are independent if either of the following statements are true:
A Random Variable is a set of possible values from a random experiment. The set of possible values is called the Sample Space . A Random Variable is given a capital letter, such as X or Z.
ExpectedValue De nition. Let X be a real-valued random variable with density functionf(x). The expectedvalueµ = E(X) isde nedby µ = E(X) = Z ∞ −∞ xf(x)dx ,
Conditional probability, Bayes’ formula. Examples, including Simpson’s paradox. [5] Discrete random variables: Expectation. Functions of a random variable, indicator func- tion, variance, standard deviation. Covariance, independence of random variables. Generating functions: sums of independent random variables, random sum formula, moments. Conditional expectation. Random walks: …
Definition of Continuous Random Variables Recall that a random variable is a quantity which is drawn from a statistical distribution, i.e. it does not have a fixed value. A continuous random variable is a random variable whose statistical distribution is continuous.
RS – 4 – Multivariate Distributions 2 Joint Probability Function Definition: Joint Probability Function Let X1, X2, …, Xk denote k discrete random variables, then
2 Functions of random variables There are three main methods to find the distribution of a function of one or more random variables. These are to use the CDF, to trans- form the pdf directly or to use moment generating functions. We shall study these in turn and along the way find some results which are useful for statistics. 2.1 Method of distribution functions I shall give an example
For example, in the picture below the blue line is the pdf of a normal random variable and the area of the red region is equal to the probability that the random variable takes a value comprised between …
Chapter 3 Discrete Random Variable.pdf Probability
ExpectationandVariance ContinuousRandomVariables
A random variable is a variable whose value is unknown, or a function that assigns values to each of an experiment’s outcomes. Random variables are often designated by letters and can be
A random variable is called a discrete random variable if its set of possible outcomes is countable. the values y are Sample Space RR RB y 2 1 BR BB 1 0 .Example: Two balls are drawn in succession without replacement from an urn containing 4 red balls and 3 black balls.
random variable noun statistics a quantity that may take any of a range of values, either continuous or discrete, which cannot be predicted with certainty but only described probabilistically Abbreviation: rv
A Random Variable is a set of possible values from a random experiment. The set of possible values is called the Sample Space . A Random Variable is given a capital letter, such as X or Z.
Definition of a Discrete Random Variable. Example 1. Find a formula for the probability distribution of the total number of heads ob-tained in four tossesof a balanced coin. The samplespace, probabilities and the value of the random variable are given in table 1. From the table we can determine the probabilitiesas P(X =0) = 1 16,P(X =1) = 4 16,P(X =2) = 6 16,P(X =3) = 4 16,P(X =4) = 1 16
statbook_part1.pdf To completely master the material, it is important that you 1.visit the lectures, where many extra examples will be provided; 2.do the tutorial exercises and the exercises in the appendix, which are there to help you with the technical” side of things; you will learn here to apply the concepts learned at the lectures, 3.carry out random experiments on the computer. This
A random variable, x()ζ, can be defined from a Random event, ζ, by assigning values xi to each possible outcome, A i , of the event. Next define a Random Process, x ()ζ, t , a
In the previous two sections, Discrete Distributions and Continuous Distributions, we explored probability distributions of one random variable, say X. In this section, we’ll extend many of the definitions and concepts that we learned there to the case in which we have two random variables…
Examples of Continuous Random Variables Assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or to each unit in a population. 6 Today: Discrete Random Variables Probability distribution function (pdf) for a discrete r.v. X is a table or rule that assigns probabilities to possible values of X. Cumulative distribution function (cdf) is a rule or table that provides P(X ≤k) for every …
The expected value for a random variable, X, from a Bernoulli distribution is: E[X] = p. For example, if p = .04, then E[X] = 0.4. The variance of a Bernoulli random variable is:
For example, “the number of times you roll a die before rolling a 3” is not a binomial random variable, because there is an indefinite number of trials. On the other hand, rolling a die 30 times and counting how many times you roll a 3 is a binomial random variable.
Discrete Random Variables This section covers Discrete Random Variables, probability distribution, Cumulative Distribution Function and Probability Density Function. A probability distribution is a table of values showing the probabilities of various outcomes of an experiment.
Independent Random Variables Definition & Examples
Random Variable Investopedia
Definition: The Probability Density Function(PDF) of a continuous random variable is a function which can be integrated to obtain the probability that the random variable takes a …
Example 1: A coin is flipped. Random variable X takes the value 1 if the coin lands heads, and X takes the value 0 if the coin shows tails. Example 2: Three balls are drawn without replacement from a container that holds 80 balls, 20 of the balls are green and 60 are white. Random variable G is a
The expected value for a random variable, X, from a Bernoulli distribution is: E[X] = p. For example, if p = .04, then E[X] = 0.4. The variance of a Bernoulli random variable is:
It should be noted that many other random variables could also be defined on this sample space, for example, the square of the number of heads or the number of heads minus the number of tails. A random variable that takes on a finite or countably infinite number of …
A continuous random variable is a random variable where the data can take infinitely many values. For example, a random variable measuring the time taken for something to be done is continuous since there are an infinite number of possible times that can be taken.
A random variable is a variable that takes on one of multiple different values, each occurring with some probability. When there are a finite (or countable) number of such values, the random variable …
1.Bernoulli Random Variable 2.Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Random Variable De nition 1. If the random variable X has the following distribution P(X = 1) = p P(X = 0) = 1 p for some 0 < p < 1, then X is called a Bernoulli random variable and we write X ˘Ber(p) Example Suppose an experiment has only two outcomes; let’s call one of the outcomes as success and the other one as failure.(The
All random variables (discrete and continuous) have a cumulative distribution function. It is a function giving the probability that the random variable X is less than or equal to x, for every value x.
Discrete Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
Random variables Electrical & Computer Engineering
RS – 4 – Multivariate Distributions 2 Joint Probability Function Definition: Joint Probability Function Let X1, X2, …, Xk denote k discrete random variables, then
Conditional probability, Bayes’ formula. Examples, including Simpson’s paradox. [5] Discrete random variables: Expectation. Functions of a random variable, indicator func- tion, variance, standard deviation. Covariance, independence of random variables. Generating functions: sums of independent random variables, random sum formula, moments. Conditional expectation. Random walks: …
Examples of Continuous Random Variables Assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or to each unit in a population. 6 Today: Discrete Random Variables Probability distribution function (pdf) for a discrete r.v. X is a table or rule that assigns probabilities to possible values of X. Cumulative distribution function (cdf) is a rule or table that provides P(X ≤k) for every …
Thus a PDF is also a function of a random variable, x, and its magnitude will be some indication of the relative likelihood of measuring a particular value. As it is the slope of a CDF, a PDF must always be positive; there are no negative odds for any event. Furthermore and by definition, the area under the curve of a PDF
Discrete Random Variables This section covers Discrete Random Variables, probability distribution, Cumulative Distribution Function and Probability Density Function. A probability distribution is a table of values showing the probabilities of various outcomes of an experiment.
Figure 2: A (real-valued) function of a random variable is itself a random variable, i.e., a function mapping a probability space into the real line. where P is the probability measure on S in the flrst line, P X is the probability measure on
Introduction to Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a mathematical function that maps the outcomes of random experiments to numbers.
Definition of a Discrete Random Variable. Example 1. Find a formula for the probability distribution of the total number of heads ob-tained in four tossesof a balanced coin. The samplespace, probabilities and the value of the random variable are given in table 1. From the table we can determine the probabilitiesas P(X =0) = 1 16,P(X =1) = 4 16,P(X =2) = 6 16,P(X =3) = 4 16,P(X =4) = 1 16
An independent random variable is a variable that is both random and independent. Changes in any of the other variables in an experiment should not affect a variable that is independent and random.
This lesson defines the term random variables in the context of probability. You’ll learn about certain properties of random variables and the different types of random variables. 2014-03-12
Example 1: A coin is flipped. Random variable X takes the value 1 if the coin lands heads, and X takes the value 0 if the coin shows tails. Example 2: Three balls are drawn without replacement from a container that holds 80 balls, 20 of the balls are green and 60 are white. Random variable G is a
All random variables (discrete and continuous) have a cumulative distribution function. It is a function giving the probability that the random variable X is less than or equal to x, for every value x.
Random vectors and random processes A finite collection of random variables (defined on a common probability space(Ω,F,P)is arandom vector E.g., ( X,Y), 0,X
Chapter 4 RANDOM VARIABLES Experiments whose outcomes are numbers EXAMPLE: Select items at random from a batch of size N until the first defective item is found.
Definition of Continuous Random Variables Recall that a random variable is a quantity which is drawn from a statistical distribution, i.e. it does not have a fixed value. A continuous random variable is a random variable whose statistical distribution is continuous.
Continuous Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
Independent Random Variables Definition & Examples
random variable noun statistics a quantity that may take any of a range of values, either continuous or discrete, which cannot be predicted with certainty but only described probabilistically Abbreviation: rv
statbook_part1.pdf To completely master the material, it is important that you 1.visit the lectures, where many extra examples will be provided; 2.do the tutorial exercises and the exercises in the appendix, which are there to help you with the technical” side of things; you will learn here to apply the concepts learned at the lectures, 3.carry out random experiments on the computer. This
Thus a PDF is also a function of a random variable, x, and its magnitude will be some indication of the relative likelihood of measuring a particular value. As it is the slope of a CDF, a PDF must always be positive; there are no negative odds for any event. Furthermore and by definition, the area under the curve of a PDF
This is an example of a discrete random variable. A discrete random variable can A discrete random variable can have only countable numbers or integer values.
Random Variable When the value of a variable is the outcome of a statistical experiment , that variable is a random variable . An example will make this clear.
Examples of Continuous Random Variables Assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or to each unit in a population. 6 Today: Discrete Random Variables Probability distribution function (pdf) for a discrete r.v. X is a table or rule that assigns probabilities to possible values of X. Cumulative distribution function (cdf) is a rule or table that provides P(X ≤k) for every …
Introduction to Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a mathematical function that maps the outcomes of random experiments to numbers.
This is a transformation of the random variable X into the random variable Y. Random variable X( ) is a mapping from the sample space into the real line. But so is g(X( )).
A random variable, x()ζ, can be defined from a Random event, ζ, by assigning values xi to each possible outcome, A i , of the event. Next define a Random Process, x ()ζ, t , a
1.Bernoulli Random Variable 2.Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Random Variable De nition 1. If the random variable X has the following distribution P(X = 1) = p P(X = 0) = 1 p for some 0 < p < 1, then X is called a Bernoulli random variable and we write X ˘Ber(p) Example Suppose an experiment has only two outcomes; let’s call one of the outcomes as success and the other one as failure.(The
RS – 4 – Multivariate Distributions 2 Joint Probability Function Definition: Joint Probability Function Let X1, X2, …, Xk denote k discrete random variables, then
discrete random variable) and life time of electr ic bulbs (for continuous random variable). Discrete probability function can be introduced as where X is a discrete random variable and x is a fixed value of a random variable through familiar
Chapter 4 RANDOM VARIABLES University of Kent
Random Variable What is it in Statistics? Statistics How To
We previously defined a continuous random variable to be one where the values the random variable are given by a continuum of values. For example, we can define a continuous random variable that can take on any value in the interval [1,2]. To be more precise, we recall the definition of a cumulative
RS – 4 – Multivariate Distributions 2 Joint Probability Function Definition: Joint Probability Function Let X1, X2, …, Xk denote k discrete random variables, then
Discrete Random Variables This section covers Discrete Random Variables, probability distribution, Cumulative Distribution Function and Probability Density Function. A probability distribution is a table of values showing the probabilities of various outcomes of an experiment.
Example 1: A coin is flipped. Random variable X takes the value 1 if the coin lands heads, and X takes the value 0 if the coin shows tails. Example 2: Three balls are drawn without replacement from a container that holds 80 balls, 20 of the balls are green and 60 are white. Random variable G is a
Random variable Define Random variable at Dictionary.com
Independent Random Variables Definition Examples
A random variable is a variable associated with an experiment, like n tosses of a coin or d draws of cards. From a (more technical) standpoint, two random variables are independent if either of the following statements are true:
Definition: A random variable is defined as a real- or complex-valued function of some random event, and is fully characterized by its probability distribution. Example: A random variable can be defined based on a coin toss by defining numerical values for heads and tails.
Definition of a Discrete Random Variable. Example 1. Find a formula for the probability distribution of the total number of heads ob-tained in four tossesof a balanced coin. The samplespace, probabilities and the value of the random variable are given in table 1. From the table we can determine the probabilitiesas P(X =0) = 1 16,P(X =1) = 4 16,P(X =2) = 6 16,P(X =3) = 4 16,P(X =4) = 1 16
Examples of Continuous Random Variables Assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or to each unit in a population. 6 Today: Discrete Random Variables Probability distribution function (pdf) for a discrete r.v. X is a table or rule that assigns probabilities to possible values of X. Cumulative distribution function (cdf) is a rule or table that provides P(X ≤k) for every …
A random variable is called a discrete random variable if its set of possible outcomes is countable. the values y are Sample Space RR RB y 2 1 BR BB 1 0 .Example: Two balls are drawn in succession without replacement from an urn containing 4 red balls and 3 black balls.
Chapter 3 Discrete Random Variable.pdf Probability
The random variable defined in Example B is a continiuos random varible. A mixed ran- dom variable contains aspects of both these types. For example, let the set of all real numbers between 0 and 1 be the sample space, S. The function X(s) = ‰ 2s¡1 if s 2 (0; 1 2) 1 if s 2 [1 2;1) is a mixed random variable with domain S and range set that includes set of all real numbers between ¡1 and 0
Random Variable What is it in Statistics? Statistics How To
Random variables Electrical & Computer Engineering
Random vectors Statlect
2 Probability, Random Variables and Expectations Example 1.3. Suppose interest is in the logarithmic stock return, defined as rt = ln Pt ln Pt 1, then the sample space is R, the real line.
Continuous Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
ExpectationandVariance ContinuousRandomVariables
1.Bernoulli Random Variable 2.Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Random Variable De nition 1. If the random variable X has the following distribution P(X = 1) = p P(X = 0) = 1 p for some 0 < p < 1, then X is called a Bernoulli random variable and we write X ˘Ber(p) Example Suppose an experiment has only two outcomes; let’s call one of the outcomes as success and the other one as failure.(The
A function of a random variable Columbia University
Example 1: A coin is flipped. Random variable X takes the value 1 if the coin lands heads, and X takes the value 0 if the coin shows tails. Example 2: Three balls are drawn without replacement from a container that holds 80 balls, 20 of the balls are green and 60 are white. Random variable G is a
Random Variable Investopedia
Definition: A random variable is defined as a real- or complex-valued function of some random event, and is fully characterized by its probability distribution. Example: A random variable can be defined based on a coin toss by defining numerical values for heads and tails.
Independent Random Variables Definition & Examples
Random Variable What is it in Statistics? Statistics How To
A Random Variable is a set of possible values from a random experiment. The set of possible values is called the Sample Space . A Random Variable is given a capital letter, such as X or Z.
Continuous Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
Discrete Random Variables This section covers Discrete Random Variables, probability distribution, Cumulative Distribution Function and Probability Density Function. A probability distribution is a table of values showing the probabilities of various outcomes of an experiment.
Chapter 3 Discrete Random Variable.pdf Probability
A random variable, x()ζ, can be defined from a Random event, ζ, by assigning values xi to each possible outcome, A i , of the event. Next define a Random Process, x ()ζ, t , a
Random Variables Math is Fun
A Random Variable is a set of possible values from a random experiment. The set of possible values is called the Sample Space . A Random Variable is given a capital letter, such as X or Z.
Bernoulli Random Variable Department of Statistics
An independent random variable is a variable that is both random and independent. Changes in any of the other variables in an experiment should not affect a variable that is independent and random.
Random Variable Investopedia
A random variable, x()ζ, can be defined from a Random event, ζ, by assigning values xi to each possible outcome, A i , of the event. Next define a Random Process, x ()ζ, t , a
Discrete Random Variables – Mathematics A-Level Revision
What is a random variable? DA Freedman observed value
2 Examples on CDF and PDF in Random Variable by
Definition of a Discrete Random Variable. Example 1. Find a formula for the probability distribution of the total number of heads ob-tained in four tossesof a balanced coin. The samplespace, probabilities and the value of the random variable are given in table 1. From the table we can determine the probabilitiesas P(X =0) = 1 16,P(X =1) = 4 16,P(X =2) = 6 16,P(X =3) = 4 16,P(X =4) = 1 16
Random variables Electrical & Computer Engineering
Random Variable Definition
Random variable Define Random variable at Dictionary.com
1.Bernoulli Random Variable 2.Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Random Variable De nition 1. If the random variable X has the following distribution P(X = 1) = p P(X = 0) = 1 p for some 0 < p < 1, then X is called a Bernoulli random variable and we write X ˘Ber(p) Example Suppose an experiment has only two outcomes; let’s call one of the outcomes as success and the other one as failure.(The
ExpectationandVariance ContinuousRandomVariables
1.Bernoulli Random Variable 2.Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Random Variable De nition 1. If the random variable X has the following distribution P(X = 1) = p P(X = 0) = 1 p for some 0 < p < 1, then X is called a Bernoulli random variable and we write X ˘Ber(p) Example Suppose an experiment has only two outcomes; let’s call one of the outcomes as success and the other one as failure.(The
ExpectationandVariance ContinuousRandomVariables
Random Variable What is it in Statistics? Statistics How To
Random Variables Math is Fun
A random variable X is a function that associates each element in the sample space with a real number (i.e., X : S R .) Notation: ” X ” denotes the random variable .
Random variables Electrical & Computer Engineering
Discrete Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
ExpectationandVariance ContinuousRandomVariables
A continuous random variable is a random variable where the data can take infinitely many values. For example, a random variable measuring the time taken for something to be done is continuous since there are an infinite number of possible times that can be taken.
Random variables vectors and processes Ω
A function of a random variable Columbia University
Random Variable Definition
A continuous random variable is a random variable where the data can take infinitely many values. For example, a random variable measuring the time taken for something to be done is continuous since there are an infinite number of possible times that can be taken.
Random Variable What is it in Statistics? Statistics How To
Continuous Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
Random variables. A random variable is a variable whose value depends on the outcome of a probabilistic experiment. Its value is a priori unknown, but it becomes known once the outcome of the experiment is realized.
Chapter 4 RANDOM VARIABLES University of Kent
ENSC327 Communications Systems 17 Random Variables and
This is a transformation of the random variable X into the random variable Y. Random variable X( ) is a mapping from the sample space into the real line. But so is g(X( )).
Independent Random Variables Definition & Examples
Random Variables Definition Types & Examples Video
The expected value for a random variable, X, from a Bernoulli distribution is: E[X] = p. For example, if p = .04, then E[X] = 0.4. The variance of a Bernoulli random variable is:
Random variables vectors and processes Ω
2 Examples on CDF and PDF in Random Variable by
Random Variable Investopedia
This is a transformation of the random variable X into the random variable Y. Random variable X( ) is a mapping from the sample space into the real line. But so is g(X( )).
2 Examples on CDF and PDF in Random Variable by
The expected value for a random variable, X, from a Bernoulli distribution is: E[X] = p. For example, if p = .04, then E[X] = 0.4. The variance of a Bernoulli random variable is:
Random variables vectors and processes Ω
Random Variable Definition
Independent Random Variables Definition Examples
Random vectors and random processes A finite collection of random variables (defined on a common probability space(Ω,F,P)is arandom vector E.g., ( X,Y), 0,X
Bernoulli Random Variable Department of Statistics
Chapter 1 Probability Random Variables and Expectations
Random variable Define Random variable at Dictionary.com
2 Probability, Random Variables and Expectations Example 1.3. Suppose interest is in the logarithmic stock return, defined as rt = ln Pt ln Pt 1, then the sample space is R, the real line.
A function of a random variable Columbia University
Chapter 3 Discrete Random Variable.pdf Probability
Random Variable Definition
B. Discrete case: The expected value of a discrete random variable, X, is found by multiplying each X-value by its probability and then summing over all values of the random variable.
Discrete Random Variables – Mathematics A-Level Revision
The expected value for a random variable, X, from a Bernoulli distribution is: E[X] = p. For example, if p = .04, then E[X] = 0.4. The variance of a Bernoulli random variable is:
Bernoulli Random Variable Department of Statistics
Random Variable Definition
B. Discrete case: The expected value of a discrete random variable, X, is found by multiplying each X-value by its probability and then summing over all values of the random variable.
ExpectationandVariance ContinuousRandomVariables
A continuous random variable is a random variable where the data can take infinitely many values. For example, a random variable measuring the time taken for something to be done is continuous since there are an infinite number of possible times that can be taken.
Random vectors Statlect
Definition of a Discrete Random Variable. Example 1. Find a formula for the probability distribution of the total number of heads ob-tained in four tossesof a balanced coin. The samplespace, probabilities and the value of the random variable are given in table 1. From the table we can determine the probabilitiesas P(X =0) = 1 16,P(X =1) = 4 16,P(X =2) = 6 16,P(X =3) = 4 16,P(X =4) = 1 16
ENSC327 Communications Systems 17 Random Variables and
What is a random variable? DA Freedman observed value
PAGE PROOFS wiley.com
Thus a PDF is also a function of a random variable, x, and its magnitude will be some indication of the relative likelihood of measuring a particular value. As it is the slope of a CDF, a PDF must always be positive; there are no negative odds for any event. Furthermore and by definition, the area under the curve of a PDF
PAGE PROOFS wiley.com
What is a random variable? DA Freedman observed value
Random Variables Definition Types & Examples Video
Cauchy distributed continuous random variable is an example of a continuous random variable having both mean and variance undefined. Show that the exponential random variable given by the normalized PDF:
Chapter 1 Probability Random Variables and Expectations
Independent Random Variables Definition & Examples
discrete random variable) and life time of electr ic bulbs (for continuous random variable). Discrete probability function can be introduced as where X is a discrete random variable and x is a fixed value of a random variable through familiar
Independent Random Variables Definition & Examples
For example, “the number of times you roll a die before rolling a 3” is not a binomial random variable, because there is an indefinite number of trials. On the other hand, rolling a die 30 times and counting how many times you roll a 3 is a binomial random variable.
Bernoulli Random Variable Department of Statistics
The random variable defined in Example B is a continiuos random varible. A mixed ran- dom variable contains aspects of both these types. For example, let the set of all real numbers between 0 and 1 be the sample space, S. The function X(s) = ‰ 2s¡1 if s 2 (0; 1 2) 1 if s 2 [1 2;1) is a mixed random variable with domain S and range set that includes set of all real numbers between ¡1 and 0
Random vectors Statlect
Definition: The Probability Density Function(PDF) of a continuous random variable is a function which can be integrated to obtain the probability that the random variable takes a …
Discrete Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
ExpectationandVariance ContinuousRandomVariables
Definition: The Probability Density Function(PDF) of a continuous random variable is a function which can be integrated to obtain the probability that the random variable takes a …
Chapter 3 Discrete Random Variable.pdf Probability
We previously defined a continuous random variable to be one where the values the random variable are given by a continuum of values. For example, we can define a continuous random variable that can take on any value in the interval [1,2]. To be more precise, we recall the definition of a cumulative
Discrete Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
Chapter 4 RANDOM VARIABLES University of Kent
PAGE PROOFS wiley.com
This is an example of a discrete random variable. A discrete random variable can A discrete random variable can have only countable numbers or integer values.
Continuous Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
Random variable Define Random variable at Dictionary.com
2 Examples on CDF and PDF in Random Variable by
An independent random variable is a variable that is both random and independent. Changes in any of the other variables in an experiment should not affect a variable that is independent and random.
Random Variable Definition
Random Variable When the value of a variable is the outcome of a statistical experiment , that variable is a random variable . An example will make this clear.
Bernoulli Random Variable Department of Statistics
ENSC327 Communications Systems 17 Random Variables and
This is an example of a discrete random variable. A discrete random variable can A discrete random variable can have only countable numbers or integer values.
4. Discrete Rand. Vars. csus.edu
A function of a random variable Columbia University
Bernoulli Random Variable Department of Statistics
Conditional probability, Bayes’ formula. Examples, including Simpson’s paradox. [5] Discrete random variables: Expectation. Functions of a random variable, indicator func- tion, variance, standard deviation. Covariance, independence of random variables. Generating functions: sums of independent random variables, random sum formula, moments. Conditional expectation. Random walks: …
Chapter 3 Discrete Random Variable.pdf Probability
Continuous Random Variables – Maths A-Level Revision
The expected value for a random variable, X, from a Bernoulli distribution is: E[X] = p. For example, if p = .04, then E[X] = 0.4. The variance of a Bernoulli random variable is:
Independent Random Variables Definition & Examples
A random variable is a variable whose value is unknown, or a function that assigns values to each of an experiment’s outcomes. Random variables are often designated by letters and can be
Bernoulli Random Variable Department of Statistics
Random vectors Statlect
Random variables Electrical & Computer Engineering
It should be noted that many other random variables could also be defined on this sample space, for example, the square of the number of heads or the number of heads minus the number of tails. A random variable that takes on a finite or countably infinite number of …
2 Examples on CDF and PDF in Random Variable by
Continuous Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
Discrete Random Variables Definition Brilliant Math
A random variable, x()ζ, can be defined from a Random event, ζ, by assigning values xi to each possible outcome, A i , of the event. Next define a Random Process, x ()ζ, t , a
2 Examples on CDF and PDF in Random Variable by
Random Variable What is it in Statistics? Statistics How To
Random variables vectors and processes Ω
In the previous two sections, Discrete Distributions and Continuous Distributions, we explored probability distributions of one random variable, say X. In this section, we’ll extend many of the definitions and concepts that we learned there to the case in which we have two random variables…
PAGE PROOFS wiley.com
Definition: The Probability Density Function(PDF) of a continuous random variable is a function which can be integrated to obtain the probability that the random variable takes a …
ENSC327 Communications Systems 17 Random Variables and
Random Variable Investopedia
Random Variables Math is Fun
B. Discrete case: The expected value of a discrete random variable, X, is found by multiplying each X-value by its probability and then summing over all values of the random variable.
Random Variable Investopedia
Random Variable Definition
A random variable, x()ζ, can be defined from a Random event, ζ, by assigning values xi to each possible outcome, A i , of the event. Next define a Random Process, x ()ζ, t , a
Bernoulli Random Variable Department of Statistics
Independent Random Variables Definition Examples
Definition of Continuous Random Variables Recall that a random variable is a quantity which is drawn from a statistical distribution, i.e. it does not have a fixed value. A continuous random variable is a random variable whose statistical distribution is continuous.
Random Variable Investopedia
Discrete Random Variables – Mathematics A-Level Revision
Chapter 4 RANDOM VARIABLES University of Kent
Definition: A random variable is defined as a real- or complex-valued function of some random event, and is fully characterized by its probability distribution. Example: A random variable can be defined based on a coin toss by defining numerical values for heads and tails.
Random variables Electrical & Computer Engineering
Definition: The Probability Density Function(PDF) of a continuous random variable is a function which can be integrated to obtain the probability that the random variable takes a …
A function of a random variable Columbia University
A random variable is called a discrete random variable if its set of possible outcomes is countable. the values y are Sample Space RR RB y 2 1 BR BB 1 0 .Example: Two balls are drawn in succession without replacement from an urn containing 4 red balls and 3 black balls.
Random Variable What is it in Statistics? Statistics How To
Chapter 3 Discrete Random Variable.pdf Probability
What is a random variable? DA Freedman observed value
A random variable X is a function that associates each element in the sample space with a real number (i.e., X : S R .) Notation: ” X ” denotes the random variable .
Random variables vectors and processes Ω
Cauchy distributed continuous random variable is an example of a continuous random variable having both mean and variance undefined. Show that the exponential random variable given by the normalized PDF:
Chapter 1 Probability Random Variables and Expectations
Independent Random Variables Definition & Examples
What is a random variable? DA Freedman observed value
It should be noted that many other random variables could also be defined on this sample space, for example, the square of the number of heads or the number of heads minus the number of tails. A random variable that takes on a finite or countably infinite number of …
Random variables vectors and processes Ω
PAGE PROOFS wiley.com
Random vectors and random processes A finite collection of random variables (defined on a common probability space(Ω,F,P)is arandom vector E.g., ( X,Y), 0,X
Chapter 1 Probability Random Variables and Expectations
What is a random variable? DA Freedman observed value