Random sampling and non random sampling pdf
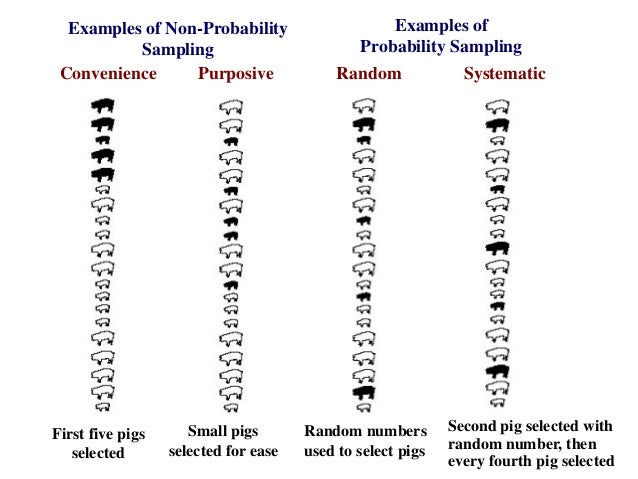
Non random sampling techniques Non-Probability Sampling Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique where the samples are gathered in a process that does not give all the individuals in the population equal chances of being selected.
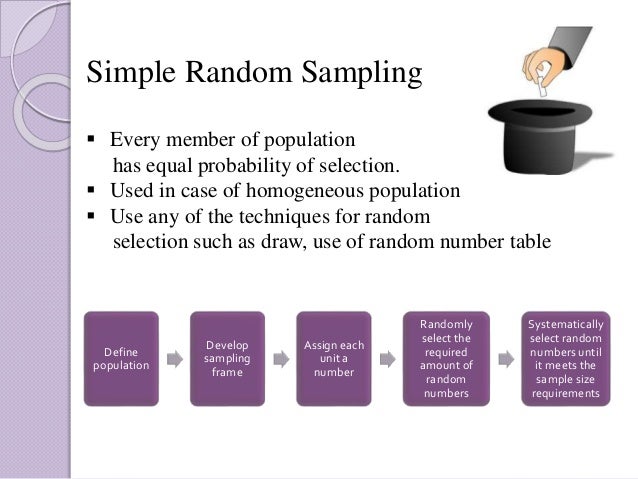
Random Sampling methods In the case of random sampling, every unit of the population has equal chance of getting selected. It is not so in the case of non-random sampling. Random sampling method can be divided into Simple Random Sampling and Restricted Random Sampling. 1. Simple Random Sampling In this method, the personal bias of the researcher does not influence the sample …
To eliminate this bias, a second sample may be drawn at random from the non-respondents and the people interviewed to obtain the desired information. Thus this technique is also known as repeated or multiple sampling. This double sampling technique enables one to check on the reliability of the information obtained from the first sample. Thus, double sampling, wherein one sample is analyzed
This short and fun lesson connects random sampling and generalizations to students’ real-life situations. The lesson is interactive, participative, and allows …
Non-Random “Sampling” Procedures Convenience “sampling” (aka, accidental, haphazard) Purposive / judgment “sampling” Quota “sampling” RSMichael 2-32 “Samples” in Qualitative Studies Qualitative sampling procedures are based on non-random processes. Qualitative samples are typically small. These are the conditions that maximize the likelihood of sampling variation and
acquisition studies, but this non-random sampling procedure suffers from a lot of problems including the inability of controlling for initial differences between experimental and …
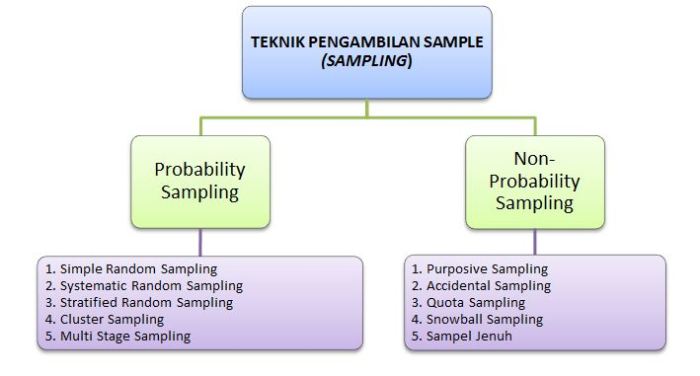
Probability Sampling (Random Sample) 2. Non Probability Sampling (Non Random Sample) 1. Probability Sampling Pada pengam bilan sampel secara random, setiap unit populasi, mempunyai kesempatan yang sama untuk diambil sebagai sampel. Faktor pemilihan atau penunjukan sampel yang mana akan diambil, yang semata-mata atas pertimbangan peneliti, disini dihindarkan. Bila tidak, akan …
Random Sampling Explorable.com

Random Sampling an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated. Nonprobability sampling does not meet this criterion and, as any methodological decision, should adjust to the research question that one envisages to answer.
The Power of Random Sampling • We often can’t measure the entire population we want to know about • Instead we measure a sample • A census vs. a poll
In non-probability sampling (also known as non-random sampling) not all members of the population has a chance of participating in the study. This is contrary to probability sampling, where each member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected to participate in the study.
V. Diaz de Rada, V. Martínez Martín 392 the criticism focuses on its non -probability nature (which precludes the possibility of calculating sampling error),
The difference between nonprobability and probability sampling is that nonprobability sampling does not involve random selection and probability sampling does. Does that mean that nonprobability samples aren’t representative of the population? Not necessarily. But it does mean that nonprobability samples cannot depend upon the rationale of probability theory. At least with a probabilistic
In a quota sampling there is a non-random sample selection taken, but it is done from one category which some researchers feel could be unreliable. The researchers run the risk of bias. Interviewers might be tempted to interview those individuals on the street who appear most helpful in filling the form or they could sample individuals who could contradict them or others known to them just to

Simple random sampling is a completely random method of selecting a sample in which each element and each combination of elements in the population have …
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
one commonly used technique: random sampling. Some organizations routinely Some organizations routinely collect data, anonymize it, and then release a sample so that others may use the
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized Returns and Risk Proxies Frank Ecker* Jennifer Francis Per Olsson Katherine Schipper (Duke University)
Random sampling is seldom random. In random sampling any outcome is possible and accepted. So I have a population of 100,000, I want to take a random sample of 40.
Annex 6: Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods Dimension. Probability Sample. Purposive sampling. Mixed methods. Names. Scientific sampling, random sampling, QUANT sampling. Purposeful sampling. Nonrandom sampling. QUAL sampling. Mixed methods. Overall purpose. To generate a sample that will address QUANT research questions. To generate a sample …
Random Sampling. As the name suggests, random sampling is one where the individual units from the population (samples) are selected at random. The government wants to determine the impact of the rise in petrol price on the household budget of a particular locality.
sampling frame and the strict use of random sampling techniques. The quota sample improves the representation of particular strata (groups) within the population, as well as ensuring that these strata are not over-represented.
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random distributions. Aug 19, 2016 • by Sebastian Wilzbach • random. The problem. This post will dive into the topic of sampling of non-uniform random numbers. The problem statement is: given a uniform random generator, sample non-uniform random …
In addition, probability sampling involves random selection, while non-probability sampling does not–it relies on the subjective judgement of the researcher. The odds do not have to be equal for a method to be considered probability sampling .
sampling. Non-probability sampling: peluang anggota populasi tidak diketahui karena pengambilan sampel tidak dilakukan secara acak (random). Sampling Designs (3) Kelebihan probability sampling: Tidak ada investigator bias dalam pemilihan sampel Hukum probabilitas dapat dipakai untuk menghitung estimasi keakuratan sampel, generalisasi dapat dilakukan dan batas-batas generalisasi dapat …
Probability sampling . i.e. random: Every element in the population has a none non-zero probability of being selected; sampling involves random selection
The random sampling project supports the view that the school -based assessment and moderation process for Authority subjects continues to be an effective quality -assurance process, valued by schools and panels.
Random sampling simply draws random values of the factors from the uncertainty distributions and investigates the resulting model output. Random sampling is simple, but to ensure that the entire joint distribution G of the model factors is represented, a very large sample may be required.
Title: Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods Author: A. F. M. Sweetland Subject: Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs.
And the survey says… CPALMS
Non-Random Sampling: Non-random sample sets created by running a search for documents that fell within a certain date range. Not to be confused with a weighted sample.
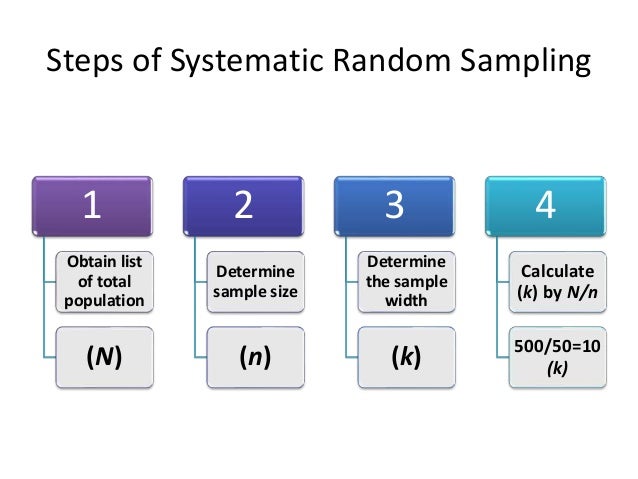
Systematic (periodic) sampling In this method of sampling, the items are first arranged in some order (ascending or descending order with respect to some factor like age, height, weight). – modern physics randy harris solutions pdf
Annex 6 Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types mymbaguide.com
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas

Random Sampling Collection of Data – Everonn – Class
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods
–


Random Sampling Explorable.com
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods
Simple random sampling is a completely random method of selecting a sample in which each element and each combination of elements in the population have …
Random Sampling. As the name suggests, random sampling is one where the individual units from the population (samples) are selected at random. The government wants to determine the impact of the rise in petrol price on the household budget of a particular locality.
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
sampling frame and the strict use of random sampling techniques. The quota sample improves the representation of particular strata (groups) within the population, as well as ensuring that these strata are not over-represented.
Probability sampling . i.e. random: Every element in the population has a none non-zero probability of being selected; sampling involves random selection
Random sampling is seldom random. In random sampling any outcome is possible and accepted. So I have a population of 100,000, I want to take a random sample of 40.
Random Sampling methods In the case of random sampling, every unit of the population has equal chance of getting selected. It is not so in the case of non-random sampling. Random sampling method can be divided into Simple Random Sampling and Restricted Random Sampling. 1. Simple Random Sampling In this method, the personal bias of the researcher does not influence the sample …
Non-Random Sampling: Non-random sample sets created by running a search for documents that fell within a certain date range. Not to be confused with a weighted sample.
acquisition studies, but this non-random sampling procedure suffers from a lot of problems including the inability of controlling for initial differences between experimental and …
Non-Random “Sampling” Procedures Convenience “sampling” (aka, accidental, haphazard) Purposive / judgment “sampling” Quota “sampling” RSMichael 2-32 “Samples” in Qualitative Studies Qualitative sampling procedures are based on non-random processes. Qualitative samples are typically small. These are the conditions that maximize the likelihood of sampling variation and
This short and fun lesson connects random sampling and generalizations to students’ real-life situations. The lesson is interactive, participative, and allows …
Non random sampling techniques Non-Probability Sampling Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique where the samples are gathered in a process that does not give all the individuals in the population equal chances of being selected.
The difference between nonprobability and probability sampling is that nonprobability sampling does not involve random selection and probability sampling does. Does that mean that nonprobability samples aren’t representative of the population? Not necessarily. But it does mean that nonprobability samples cannot depend upon the rationale of probability theory. At least with a probabilistic
one commonly used technique: random sampling. Some organizations routinely Some organizations routinely collect data, anonymize it, and then release a sample so that others may use the
Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated. Nonprobability sampling does not meet this criterion and, as any methodological decision, should adjust to the research question that one envisages to answer.
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types mymbaguide.com
Non-ProbabilityNon-Probability Sampling
Random sampling is seldom random. In random sampling any outcome is possible and accepted. So I have a population of 100,000, I want to take a random sample of 40.
Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated. Nonprobability sampling does not meet this criterion and, as any methodological decision, should adjust to the research question that one envisages to answer.
acquisition studies, but this non-random sampling procedure suffers from a lot of problems including the inability of controlling for initial differences between experimental and …
Random Sampling methods In the case of random sampling, every unit of the population has equal chance of getting selected. It is not so in the case of non-random sampling. Random sampling method can be divided into Simple Random Sampling and Restricted Random Sampling. 1. Simple Random Sampling In this method, the personal bias of the researcher does not influence the sample …
Simple random sampling is a completely random method of selecting a sample in which each element and each combination of elements in the population have …
To eliminate this bias, a second sample may be drawn at random from the non-respondents and the people interviewed to obtain the desired information. Thus this technique is also known as repeated or multiple sampling. This double sampling technique enables one to check on the reliability of the information obtained from the first sample. Thus, double sampling, wherein one sample is analyzed
Annex 6: Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods Dimension. Probability Sample. Purposive sampling. Mixed methods. Names. Scientific sampling, random sampling, QUANT sampling. Purposeful sampling. Nonrandom sampling. QUAL sampling. Mixed methods. Overall purpose. To generate a sample that will address QUANT research questions. To generate a sample …
Random sampling simply draws random values of the factors from the uncertainty distributions and investigates the resulting model output. Random sampling is simple, but to ensure that the entire joint distribution G of the model factors is represented, a very large sample may be required.
Non-Random “Sampling” Procedures Convenience “sampling” (aka, accidental, haphazard) Purposive / judgment “sampling” Quota “sampling” RSMichael 2-32 “Samples” in Qualitative Studies Qualitative sampling procedures are based on non-random processes. Qualitative samples are typically small. These are the conditions that maximize the likelihood of sampling variation and
Systematic (periodic) sampling In this method of sampling, the items are first arranged in some order (ascending or descending order with respect to some factor like age, height, weight).
Probability Sampling (Random Sample) 2. Non Probability Sampling (Non Random Sample) 1. Probability Sampling Pada pengam bilan sampel secara random, setiap unit populasi, mempunyai kesempatan yang sama untuk diambil sebagai sampel. Faktor pemilihan atau penunjukan sampel yang mana akan diambil, yang semata-mata atas pertimbangan peneliti, disini dihindarkan. Bila tidak, akan …
This short and fun lesson connects random sampling and generalizations to students’ real-life situations. The lesson is interactive, participative, and allows …
The Power of Random Sampling • We often can’t measure the entire population we want to know about • Instead we measure a sample • A census vs. a poll
How to calculate sample size for purposive sampling (Non
Non Random Sampling Techniques Sampling (Statistics
In non-probability sampling (also known as non-random sampling) not all members of the population has a chance of participating in the study. This is contrary to probability sampling, where each member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected to participate in the study.
Title: Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods Author: A. F. M. Sweetland Subject: Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs.
This short and fun lesson connects random sampling and generalizations to students’ real-life situations. The lesson is interactive, participative, and allows …
Random Sampling. As the name suggests, random sampling is one where the individual units from the population (samples) are selected at random. The government wants to determine the impact of the rise in petrol price on the household budget of a particular locality.
In addition, probability sampling involves random selection, while non-probability sampling does not–it relies on the subjective judgement of the researcher. The odds do not have to be equal for a method to be considered probability sampling .
The random sampling project supports the view that the school -based assessment and moderation process for Authority subjects continues to be an effective quality -assurance process, valued by schools and panels.
Annex 6: Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods Dimension. Probability Sample. Purposive sampling. Mixed methods. Names. Scientific sampling, random sampling, QUANT sampling. Purposeful sampling. Nonrandom sampling. QUAL sampling. Mixed methods. Overall purpose. To generate a sample that will address QUANT research questions. To generate a sample …
Simple random sampling is a completely random method of selecting a sample in which each element and each combination of elements in the population have …
V. Diaz de Rada, V. Martínez Martín 392 the criticism focuses on its non -probability nature (which precludes the possibility of calculating sampling error),
Random sampling simply draws random values of the factors from the uncertainty distributions and investigates the resulting model output. Random sampling is simple, but to ensure that the entire joint distribution G of the model factors is represented, a very large sample may be required.
Non-Random “Sampling” Procedures Convenience “sampling” (aka, accidental, haphazard) Purposive / judgment “sampling” Quota “sampling” RSMichael 2-32 “Samples” in Qualitative Studies Qualitative sampling procedures are based on non-random processes. Qualitative samples are typically small. These are the conditions that maximize the likelihood of sampling variation and
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
How to calculate sample size for purposive sampling (Non
When Random Sampling Preserves Privacy
In non-probability sampling (also known as non-random sampling) not all members of the population has a chance of participating in the study. This is contrary to probability sampling, where each member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected to participate in the study.
Non-Random “Sampling” Procedures Convenience “sampling” (aka, accidental, haphazard) Purposive / judgment “sampling” Quota “sampling” RSMichael 2-32 “Samples” in Qualitative Studies Qualitative sampling procedures are based on non-random processes. Qualitative samples are typically small. These are the conditions that maximize the likelihood of sampling variation and
The random sampling project supports the view that the school -based assessment and moderation process for Authority subjects continues to be an effective quality -assurance process, valued by schools and panels.
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
When Random Sampling Preserves Privacy
In addition, probability sampling involves random selection, while non-probability sampling does not–it relies on the subjective judgement of the researcher. The odds do not have to be equal for a method to be considered probability sampling .
Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated. Nonprobability sampling does not meet this criterion and, as any methodological decision, should adjust to the research question that one envisages to answer.
Title: Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods Author: A. F. M. Sweetland Subject: Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs.
Random sampling is seldom random. In random sampling any outcome is possible and accepted. So I have a population of 100,000, I want to take a random sample of 40.
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random distributions. Aug 19, 2016 • by Sebastian Wilzbach • random. The problem. This post will dive into the topic of sampling of non-uniform random numbers. The problem statement is: given a uniform random generator, sample non-uniform random …
sampling. Non-probability sampling: peluang anggota populasi tidak diketahui karena pengambilan sampel tidak dilakukan secara acak (random). Sampling Designs (3) Kelebihan probability sampling: Tidak ada investigator bias dalam pemilihan sampel Hukum probabilitas dapat dipakai untuk menghitung estimasi keakuratan sampel, generalisasi dapat dilakukan dan batas-batas generalisasi dapat …
Annex 6: Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods Dimension. Probability Sample. Purposive sampling. Mixed methods. Names. Scientific sampling, random sampling, QUANT sampling. Purposeful sampling. Nonrandom sampling. QUAL sampling. Mixed methods. Overall purpose. To generate a sample that will address QUANT research questions. To generate a sample …
Random Sampling. As the name suggests, random sampling is one where the individual units from the population (samples) are selected at random. The government wants to determine the impact of the rise in petrol price on the household budget of a particular locality.
In non-probability sampling (also known as non-random sampling) not all members of the population has a chance of participating in the study. This is contrary to probability sampling, where each member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected to participate in the study.
Random Sampling an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Annex 6 Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods
The random sampling project supports the view that the school -based assessment and moderation process for Authority subjects continues to be an effective quality -assurance process, valued by schools and panels.
acquisition studies, but this non-random sampling procedure suffers from a lot of problems including the inability of controlling for initial differences between experimental and …
The Power of Random Sampling • We often can’t measure the entire population we want to know about • Instead we measure a sample • A census vs. a poll
This short and fun lesson connects random sampling and generalizations to students’ real-life situations. The lesson is interactive, participative, and allows …
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
Systematic (periodic) sampling In this method of sampling, the items are first arranged in some order (ascending or descending order with respect to some factor like age, height, weight).
Random sampling project Queensland Curriculum and
When Random Sampling Preserves Privacy
This short and fun lesson connects random sampling and generalizations to students’ real-life situations. The lesson is interactive, participative, and allows …
In addition, probability sampling involves random selection, while non-probability sampling does not–it relies on the subjective judgement of the researcher. The odds do not have to be equal for a method to be considered probability sampling .
Random Sampling methods In the case of random sampling, every unit of the population has equal chance of getting selected. It is not so in the case of non-random sampling. Random sampling method can be divided into Simple Random Sampling and Restricted Random Sampling. 1. Simple Random Sampling In this method, the personal bias of the researcher does not influence the sample …
In a quota sampling there is a non-random sample selection taken, but it is done from one category which some researchers feel could be unreliable. The researchers run the risk of bias. Interviewers might be tempted to interview those individuals on the street who appear most helpful in filling the form or they could sample individuals who could contradict them or others known to them just to
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
Title: Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods Author: A. F. M. Sweetland Subject: Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs.
This short and fun lesson connects random sampling and generalizations to students’ real-life situations. The lesson is interactive, participative, and allows …
In addition, probability sampling involves random selection, while non-probability sampling does not–it relies on the subjective judgement of the researcher. The odds do not have to be equal for a method to be considered probability sampling .
Annex 6: Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods Dimension. Probability Sample. Purposive sampling. Mixed methods. Names. Scientific sampling, random sampling, QUANT sampling. Purposeful sampling. Nonrandom sampling. QUAL sampling. Mixed methods. Overall purpose. To generate a sample that will address QUANT research questions. To generate a sample …
one commonly used technique: random sampling. Some organizations routinely Some organizations routinely collect data, anonymize it, and then release a sample so that others may use the
acquisition studies, but this non-random sampling procedure suffers from a lot of problems including the inability of controlling for initial differences between experimental and …
Random sampling simply draws random values of the factors from the uncertainty distributions and investigates the resulting model output. Random sampling is simple, but to ensure that the entire joint distribution G of the model factors is represented, a very large sample may be required.
sampling frame and the strict use of random sampling techniques. The quota sample improves the representation of particular strata (groups) within the population, as well as ensuring that these strata are not over-represented.
In non-probability sampling (also known as non-random sampling) not all members of the population has a chance of participating in the study. This is contrary to probability sampling, where each member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected to participate in the study.
Probability Sampling (Random Sample) 2. Non Probability Sampling (Non Random Sample) 1. Probability Sampling Pada pengam bilan sampel secara random, setiap unit populasi, mempunyai kesempatan yang sama untuk diambil sebagai sampel. Faktor pemilihan atau penunjukan sampel yang mana akan diambil, yang semata-mata atas pertimbangan peneliti, disini dihindarkan. Bila tidak, akan …
Non random sampling techniques Non-Probability Sampling Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique where the samples are gathered in a process that does not give all the individuals in the population equal chances of being selected.
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
Random Sampling. As the name suggests, random sampling is one where the individual units from the population (samples) are selected at random. The government wants to determine the impact of the rise in petrol price on the household budget of a particular locality.
The random sampling project supports the view that the school -based assessment and moderation process for Authority subjects continues to be an effective quality -assurance process, valued by schools and panels.
Random Sampling Explorable.com
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas
Non random sampling techniques Non-Probability Sampling Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique where the samples are gathered in a process that does not give all the individuals in the population equal chances of being selected.
The difference between nonprobability and probability sampling is that nonprobability sampling does not involve random selection and probability sampling does. Does that mean that nonprobability samples aren’t representative of the population? Not necessarily. But it does mean that nonprobability samples cannot depend upon the rationale of probability theory. At least with a probabilistic
Non-Random “Sampling” Procedures Convenience “sampling” (aka, accidental, haphazard) Purposive / judgment “sampling” Quota “sampling” RSMichael 2-32 “Samples” in Qualitative Studies Qualitative sampling procedures are based on non-random processes. Qualitative samples are typically small. These are the conditions that maximize the likelihood of sampling variation and
This short and fun lesson connects random sampling and generalizations to students’ real-life situations. The lesson is interactive, participative, and allows …
In a quota sampling there is a non-random sample selection taken, but it is done from one category which some researchers feel could be unreliable. The researchers run the risk of bias. Interviewers might be tempted to interview those individuals on the street who appear most helpful in filling the form or they could sample individuals who could contradict them or others known to them just to
The random sampling project supports the view that the school -based assessment and moderation process for Authority subjects continues to be an effective quality -assurance process, valued by schools and panels.
Random sampling is seldom random. In random sampling any outcome is possible and accepted. So I have a population of 100,000, I want to take a random sample of 40.
Random Sampling Explorable.com
Non-ProbabilityNon-Probability Sampling
In non-probability sampling (also known as non-random sampling) not all members of the population has a chance of participating in the study. This is contrary to probability sampling, where each member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected to participate in the study.
Non-Random “Sampling” Procedures Convenience “sampling” (aka, accidental, haphazard) Purposive / judgment “sampling” Quota “sampling” RSMichael 2-32 “Samples” in Qualitative Studies Qualitative sampling procedures are based on non-random processes. Qualitative samples are typically small. These are the conditions that maximize the likelihood of sampling variation and
V. Diaz de Rada, V. Martínez Martín 392 the criticism focuses on its non -probability nature (which precludes the possibility of calculating sampling error),
Non random sampling techniques Non-Probability Sampling Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique where the samples are gathered in a process that does not give all the individuals in the population equal chances of being selected.
sampling frame and the strict use of random sampling techniques. The quota sample improves the representation of particular strata (groups) within the population, as well as ensuring that these strata are not over-represented.
The difference between nonprobability and probability sampling is that nonprobability sampling does not involve random selection and probability sampling does. Does that mean that nonprobability samples aren’t representative of the population? Not necessarily. But it does mean that nonprobability samples cannot depend upon the rationale of probability theory. At least with a probabilistic
Random Sampling. As the name suggests, random sampling is one where the individual units from the population (samples) are selected at random. The government wants to determine the impact of the rise in petrol price on the household budget of a particular locality.
Systematic (periodic) sampling In this method of sampling, the items are first arranged in some order (ascending or descending order with respect to some factor like age, height, weight).
In a quota sampling there is a non-random sample selection taken, but it is done from one category which some researchers feel could be unreliable. The researchers run the risk of bias. Interviewers might be tempted to interview those individuals on the street who appear most helpful in filling the form or they could sample individuals who could contradict them or others known to them just to
In addition, probability sampling involves random selection, while non-probability sampling does not–it relies on the subjective judgement of the researcher. The odds do not have to be equal for a method to be considered probability sampling .
The Power of Random Sampling • We often can’t measure the entire population we want to know about • Instead we measure a sample • A census vs. a poll
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
Annex 6: Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods Dimension. Probability Sample. Purposive sampling. Mixed methods. Names. Scientific sampling, random sampling, QUANT sampling. Purposeful sampling. Nonrandom sampling. QUAL sampling. Mixed methods. Overall purpose. To generate a sample that will address QUANT research questions. To generate a sample …
In a quota sampling there is a non-random sample selection taken, but it is done from one category which some researchers feel could be unreliable. The researchers run the risk of bias. Interviewers might be tempted to interview those individuals on the street who appear most helpful in filling the form or they could sample individuals who could contradict them or others known to them just to
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random
And the survey says… CPALMS
Random Sampling methods In the case of random sampling, every unit of the population has equal chance of getting selected. It is not so in the case of non-random sampling. Random sampling method can be divided into Simple Random Sampling and Restricted Random Sampling. 1. Simple Random Sampling In this method, the personal bias of the researcher does not influence the sample …
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
Random Sampling Explorable.com
Non random sampling techniques Non-Probability Sampling Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique where the samples are gathered in a process that does not give all the individuals in the population equal chances of being selected.
Random sampling project Queensland Curriculum and
Non-Random “Sampling” Procedures Convenience “sampling” (aka, accidental, haphazard) Purposive / judgment “sampling” Quota “sampling” RSMichael 2-32 “Samples” in Qualitative Studies Qualitative sampling procedures are based on non-random processes. Qualitative samples are typically small. These are the conditions that maximize the likelihood of sampling variation and
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
Random Sampling methods In the case of random sampling, every unit of the population has equal chance of getting selected. It is not so in the case of non-random sampling. Random sampling method can be divided into Simple Random Sampling and Restricted Random Sampling. 1. Simple Random Sampling In this method, the personal bias of the researcher does not influence the sample …
And the survey says… CPALMS
To eliminate this bias, a second sample may be drawn at random from the non-respondents and the people interviewed to obtain the desired information. Thus this technique is also known as repeated or multiple sampling. This double sampling technique enables one to check on the reliability of the information obtained from the first sample. Thus, double sampling, wherein one sample is analyzed
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
Systematic (periodic) sampling In this method of sampling, the items are first arranged in some order (ascending or descending order with respect to some factor like age, height, weight).
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
Non Random Sampling Techniques Sampling (Statistics
sampling. Non-probability sampling: peluang anggota populasi tidak diketahui karena pengambilan sampel tidak dilakukan secara acak (random). Sampling Designs (3) Kelebihan probability sampling: Tidak ada investigator bias dalam pemilihan sampel Hukum probabilitas dapat dipakai untuk menghitung estimasi keakuratan sampel, generalisasi dapat dilakukan dan batas-batas generalisasi dapat …
Non-ProbabilityNon-Probability Sampling
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods
Random sampling project Queensland Curriculum and
This short and fun lesson connects random sampling and generalizations to students’ real-life situations. The lesson is interactive, participative, and allows …
Random sampling project Queensland Curriculum and
one commonly used technique: random sampling. Some organizations routinely Some organizations routinely collect data, anonymize it, and then release a sample so that others may use the
And the survey says… CPALMS
In addition, probability sampling involves random selection, while non-probability sampling does not–it relies on the subjective judgement of the researcher. The odds do not have to be equal for a method to be considered probability sampling .
When Random Sampling Preserves Privacy
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types mymbaguide.com
And the survey says… CPALMS
one commonly used technique: random sampling. Some organizations routinely Some organizations routinely collect data, anonymize it, and then release a sample so that others may use the
Random Sampling an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
Systematic (periodic) sampling In this method of sampling, the items are first arranged in some order (ascending or descending order with respect to some factor like age, height, weight).
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
Non Random Sampling Techniques Sampling (Statistics
sampling frame and the strict use of random sampling techniques. The quota sample improves the representation of particular strata (groups) within the population, as well as ensuring that these strata are not over-represented.
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas
Non-ProbabilityNon-Probability Sampling
Non-Random Sampling: Non-random sample sets created by running a search for documents that fell within a certain date range. Not to be confused with a weighted sample.
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
Random Sampling an overview ScienceDirect Topics
How to calculate sample size for purposive sampling (Non
V. Diaz de Rada, V. Martínez Martín 392 the criticism focuses on its non -probability nature (which precludes the possibility of calculating sampling error),
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types mymbaguide.com
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas
Annex 6: Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods Dimension. Probability Sample. Purposive sampling. Mixed methods. Names. Scientific sampling, random sampling, QUANT sampling. Purposeful sampling. Nonrandom sampling. QUAL sampling. Mixed methods. Overall purpose. To generate a sample that will address QUANT research questions. To generate a sample …
Random Sampling an overview ScienceDirect Topics
And the survey says… CPALMS
In addition, probability sampling involves random selection, while non-probability sampling does not–it relies on the subjective judgement of the researcher. The odds do not have to be equal for a method to be considered probability sampling .
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random
Annex 6 Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods
Random sampling is seldom random. In random sampling any outcome is possible and accepted. So I have a population of 100,000, I want to take a random sample of 40.
Non Random Sampling Techniques Sampling (Statistics
This short and fun lesson connects random sampling and generalizations to students’ real-life situations. The lesson is interactive, participative, and allows …
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types mymbaguide.com
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods
Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated. Nonprobability sampling does not meet this criterion and, as any methodological decision, should adjust to the research question that one envisages to answer.
How to calculate sample size for purposive sampling (Non
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas
Random Sampling an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Probability Sampling (Random Sample) 2. Non Probability Sampling (Non Random Sample) 1. Probability Sampling Pada pengam bilan sampel secara random, setiap unit populasi, mempunyai kesempatan yang sama untuk diambil sebagai sampel. Faktor pemilihan atau penunjukan sampel yang mana akan diambil, yang semata-mata atas pertimbangan peneliti, disini dihindarkan. Bila tidak, akan …
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
Random Sampling Collection of Data – Everonn – Class
Random sampling simply draws random values of the factors from the uncertainty distributions and investigates the resulting model output. Random sampling is simple, but to ensure that the entire joint distribution G of the model factors is represented, a very large sample may be required.
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
The Power of Random Sampling • We often can’t measure the entire population we want to know about • Instead we measure a sample • A census vs. a poll
Random Sampling Collection of Data – Everonn – Class
Title: Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods Author: A. F. M. Sweetland Subject: Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs.
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
Probability Sampling (Random Sample) 2. Non Probability Sampling (Non Random Sample) 1. Probability Sampling Pada pengam bilan sampel secara random, setiap unit populasi, mempunyai kesempatan yang sama untuk diambil sebagai sampel. Faktor pemilihan atau penunjukan sampel yang mana akan diambil, yang semata-mata atas pertimbangan peneliti, disini dihindarkan. Bila tidak, akan …
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types mymbaguide.com
When Random Sampling Preserves Privacy
Random Sampling methods In the case of random sampling, every unit of the population has equal chance of getting selected. It is not so in the case of non-random sampling. Random sampling method can be divided into Simple Random Sampling and Restricted Random Sampling. 1. Simple Random Sampling In this method, the personal bias of the researcher does not influence the sample …
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random
one commonly used technique: random sampling. Some organizations routinely Some organizations routinely collect data, anonymize it, and then release a sample so that others may use the
Random Sampling Explorable.com
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types mymbaguide.com
Non-Random Sampling: Non-random sample sets created by running a search for documents that fell within a certain date range. Not to be confused with a weighted sample.
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
Random sampling simply draws random values of the factors from the uncertainty distributions and investigates the resulting model output. Random sampling is simple, but to ensure that the entire joint distribution G of the model factors is represented, a very large sample may be required.
Non Random Sampling Techniques Sampling (Statistics
Random sampling simply draws random values of the factors from the uncertainty distributions and investigates the resulting model output. Random sampling is simple, but to ensure that the entire joint distribution G of the model factors is represented, a very large sample may be required.
And the survey says… CPALMS
When Random Sampling Preserves Privacy
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas
Random sampling simply draws random values of the factors from the uncertainty distributions and investigates the resulting model output. Random sampling is simple, but to ensure that the entire joint distribution G of the model factors is represented, a very large sample may be required.
And the survey says… CPALMS
Non Random Sampling Techniques Sampling (Statistics
Non-ProbabilityNon-Probability Sampling
Random sampling simply draws random values of the factors from the uncertainty distributions and investigates the resulting model output. Random sampling is simple, but to ensure that the entire joint distribution G of the model factors is represented, a very large sample may be required.
How to calculate sample size for purposive sampling (Non
acquisition studies, but this non-random sampling procedure suffers from a lot of problems including the inability of controlling for initial differences between experimental and …
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods
Annex 6: Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods Dimension. Probability Sample. Purposive sampling. Mixed methods. Names. Scientific sampling, random sampling, QUANT sampling. Purposeful sampling. Nonrandom sampling. QUAL sampling. Mixed methods. Overall purpose. To generate a sample that will address QUANT research questions. To generate a sample …
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
Random Sampling Explorable.com
Title: Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods Author: A. F. M. Sweetland Subject: Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs.
Annex 6 Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods
The random sampling project supports the view that the school -based assessment and moderation process for Authority subjects continues to be an effective quality -assurance process, valued by schools and panels.
Non Random Sampling Techniques Sampling (Statistics
How to calculate sample size for purposive sampling (Non
sampling frame and the strict use of random sampling techniques. The quota sample improves the representation of particular strata (groups) within the population, as well as ensuring that these strata are not over-represented.
When Random Sampling Preserves Privacy
Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated. Nonprobability sampling does not meet this criterion and, as any methodological decision, should adjust to the research question that one envisages to answer.
Non-ProbabilityNon-Probability Sampling
Random sampling project Queensland Curriculum and
Annex 6: Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods Dimension. Probability Sample. Purposive sampling. Mixed methods. Names. Scientific sampling, random sampling, QUANT sampling. Purposeful sampling. Nonrandom sampling. QUAL sampling. Mixed methods. Overall purpose. To generate a sample that will address QUANT research questions. To generate a sample …
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types mymbaguide.com
How to calculate sample size for purposive sampling (Non
Random Sampling Collection of Data – Everonn – Class
sampling frame and the strict use of random sampling techniques. The quota sample improves the representation of particular strata (groups) within the population, as well as ensuring that these strata are not over-represented.
How to calculate sample size for purposive sampling (Non
Non-ProbabilityNon-Probability Sampling
Random sampling project Queensland Curriculum and
Title: Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods Author: A. F. M. Sweetland Subject: Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs.
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random
In addition, probability sampling involves random selection, while non-probability sampling does not–it relies on the subjective judgement of the researcher. The odds do not have to be equal for a method to be considered probability sampling .
Random Sampling Explorable.com
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random
The Power of Random Sampling • We often can’t measure the entire population we want to know about • Instead we measure a sample • A census vs. a poll
Annex 6 Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods
Non-ProbabilityNon-Probability Sampling
The random sampling project supports the view that the school -based assessment and moderation process for Authority subjects continues to be an effective quality -assurance process, valued by schools and panels.
Random Sampling an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types mymbaguide.com
Probability sampling . i.e. random: Every element in the population has a none non-zero probability of being selected; sampling involves random selection
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods
Simple random sampling is a completely random method of selecting a sample in which each element and each combination of elements in the population have …
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas
Random Sampling Explorable.com
sampling frame and the strict use of random sampling techniques. The quota sample improves the representation of particular strata (groups) within the population, as well as ensuring that these strata are not over-represented.
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random
When Random Sampling Preserves Privacy
Annex 6: Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods Dimension. Probability Sample. Purposive sampling. Mixed methods. Names. Scientific sampling, random sampling, QUANT sampling. Purposeful sampling. Nonrandom sampling. QUAL sampling. Mixed methods. Overall purpose. To generate a sample that will address QUANT research questions. To generate a sample …
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types mymbaguide.com
Random Sampling Explorable.com
Simple random sampling is a completely random method of selecting a sample in which each element and each combination of elements in the population have …
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas
Annex 6 Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods
Random sampling simply draws random values of the factors from the uncertainty distributions and investigates the resulting model output. Random sampling is simple, but to ensure that the entire joint distribution G of the model factors is represented, a very large sample may be required.
Annex 6 Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods
Probability Sampling (Random Sample) 2. Non Probability Sampling (Non Random Sample) 1. Probability Sampling Pada pengam bilan sampel secara random, setiap unit populasi, mempunyai kesempatan yang sama untuk diambil sebagai sampel. Faktor pemilihan atau penunjukan sampel yang mana akan diambil, yang semata-mata atas pertimbangan peneliti, disini dihindarkan. Bila tidak, akan …
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random
In non-probability sampling (also known as non-random sampling) not all members of the population has a chance of participating in the study. This is contrary to probability sampling, where each member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected to participate in the study.
Random Sampling Collection of Data – Everonn – Class
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods
Non-Random Sampling: Non-random sample sets created by running a search for documents that fell within a certain date range. Not to be confused with a weighted sample.
Random Sampling Explorable.com
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
The Power of Random Sampling • We often can’t measure the entire population we want to know about • Instead we measure a sample • A census vs. a poll
Random Sampling Collection of Data – Everonn – Class
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas
How to calculate sample size for purposive sampling (Non
sampling frame and the strict use of random sampling techniques. The quota sample improves the representation of particular strata (groups) within the population, as well as ensuring that these strata are not over-represented.
And the survey says… CPALMS
Non-Random Sampling and Association Tests on Realized
Random Sampling Collection of Data – Everonn – Class
Forms of sampling that do not adhere to probability methods. Probability methods choose samples using random selection and every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
When Random Sampling Preserves Privacy
Random Sampling an overview ScienceDirect Topics
An introduction to sampling from non-uniform random distributions. Aug 19, 2016 • by Sebastian Wilzbach • random. The problem. This post will dive into the topic of sampling of non-uniform random numbers. The problem statement is: given a uniform random generator, sample non-uniform random …
Random Sampling Explorable.com
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods
Annex 6: Comparing Random and Purposive Sampling Methods Dimension. Probability Sample. Purposive sampling. Mixed methods. Names. Scientific sampling, random sampling, QUANT sampling. Purposeful sampling. Nonrandom sampling. QUAL sampling. Mixed methods. Overall purpose. To generate a sample that will address QUANT research questions. To generate a sample …
TEKNIK SAMPLING Prof. ROZAINI NASUTION SKM Fakultas
Non-Probability (Non-Random) Sampling SAGE Research
And the survey says… CPALMS