Random and non random sampling pdf
Bias and Sampling Worksheet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. A large corporation wants to find out which benefits plan its employees would prefer. Which procedure would be most likely to obtain a statistically unbiased sample? a. survey a random sample of employees from a list of all employees b. invite all employees to
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
Nonprobability Sampling. Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population. Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated.
Methods of Restricted Random Sampling: There are three methods of restricted random sampling. (i) Stratified Sampling: This is a method for getting a more efficient sample. In this method, the total population is divided into different groups or classes, which are called Strata.
In any form of research, true random sampling is always difficult to achieve. Most researchers are bounded by time, money and workforce and because of these limitations, it is almost impossible to randomly sample the entire population and it is often necessary to employ another sampling technique, the non-probability sampling technique.
In statistics, sampling bias is a bias in which a sample is collected in such a way that some members of the intended population are less likely to be included than others. It results in a biased sample, a non-random sample of a population (or non-human factors)
random sampling impractical, it is also vital to understand the implications of using non- random sampling methods. This paper provides an overview and comparison of random and non-random sampling methods, with an emphasis on the assumptions necessary to generalize information from a non-random sample to a larger population. Additional topics discussed include site selection …
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies

Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
Non-probability sampling • Convenience sampling eg grab or opportunity sampling; –useful for pilot testing; –cannot scientifically make generalisations about the whole population from this sample. • Quota sampling –Segmented into mutually-exclusive sub-groups, then judgement is used to (non-randomly) select sample from each segment. • Purposive sampling –A limited number of
Types of non-random sampling: Non-random sampling is widely used in qualitative research. Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research. The following are non-random sampling methods: Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research.
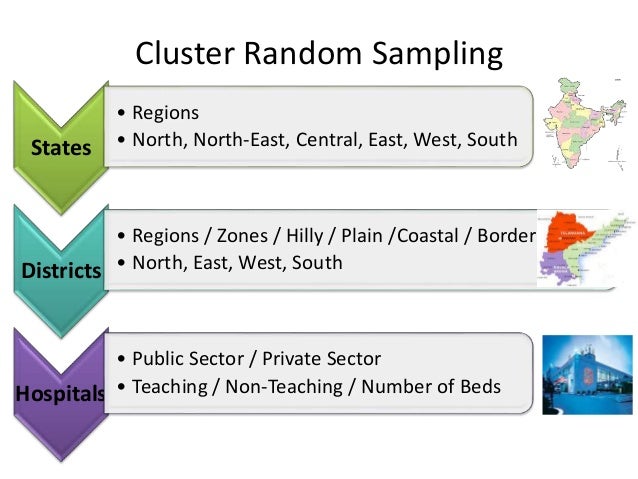
SAMPLING . Stratified Random Cluster Random . Simple Random Non-probability sampling . What are the different types of samples? What’s the difference between them? tudent. C. L. earning. S. entre. A sampling strategy where the population of interest is divided into representative “clusters” of individuals, among whom a random selection of subjects is drawn. Cluster sampling is often …
Random Sampling is considered the easiest way of sampling ways wherein all participants of a given populace have the same possibility of being selected for the example group. One strategy of assuring a random example is to allocate amounts of the populace and select the sample through unsystematic assortment of numbers. On the other hand to get the ideal random sample, the random should be
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types – My MBA Guide Mymbaguide.com Non-Random Sampling can be divided into Judgement Sampling, Convenience Sampling and Quota Sampling as detailed below. Judgement Sampling In this method, the selection of sample is done by the researcher according to his judgement.
15/04/2011 · Best Answer: Random Sampling Advantages: Since it is done at random, the whole process is unbiased. This is good to use in smaller populations, of course it doesn’t 100% protect from bias (depending on the question).
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
A stratified random sample is a population sample that requires the population to be divided into strata so that random samples can be taken from each stratum.

Clear very visual presentation covering: 1. Systematic Sampling 2. Cluster Sampling 3. Quota sampling 4. Convenience sampling 5. Advantages and disadvantages of sampling methods and problems for each of these.
Simple Random Sampling: The simplest form of random sampling is called simple random sampling. Neither of these mechanical procedures is very feasible and, with the development of inexpensive computers there is a much easier way. Simple random sampling is simple to accomplish and is easy to explain to others. Because simple random sampling is a fair way to select a sample, …
A note on random number generation Christophe Dutang and Diethelm Wuertz September 2009 1. 2 OVERVIEW OF RANDOM GENERATION ALGORITMS 2 Nothing in Nature is random… a thing appears random only through the incompleteness of our knowledge.” Spinoza, Ethics I1. 1 Introduction Random simulation has long been a very popular and well studied eld of mathematics. There exists …
Probability Sampling methodology has many kinds and turns into any actually one in every of them used for selecting random objects from the report based mostly totally on some setup and prerequisite. The Non-probability Sampling methodology is the samples collected by a course of via which the entire members belonging to the sample shouldn’t have any chance of getting select.
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING-1-DEFINITIONS Nonrandom mating: Mating individuals are more closely related or less closely related than those
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods RAND
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samp les- Independent Practice Worksheet Complete all the problems. 1. Three out of four doctors interviewed recommend aspirin. Is this a conclusion drawn from a sample or population? 2. Out of 1000 men, 940 men are married. Is this conclusion drawn from a sample or a population? 3. The average wages of a person in New City is ,000 per month. Is this
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
Difference Between Sample Mean and Population Mean Difference Between Population and Sample Difference Between Stratified and Cluster Sampling Difference Between Probability and Non-Probability Sampling Difference Between Census and Sampling Difference Between Standard Deviation and …
Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs; i.e., the method requires numbering each member of the survey population, whereas nonrandom sampling involves taking every nth member. Findings indicate that as long as
The underlying idea of non-uniform random sampling is that given an inverse function F − 1 F^{-1} F − 1 for the cumulative density function (CDF) of a target density f (x) f(x) f (x), random values can be mapped to a distribution.
Stratified sampling offers certain advantages and disadvantages compared to simple random sampling. A stratified sample can provide a more accurate representation of the …
In this section the two major types of sampling, random and non-random, will be examined. RANDOM SAMPLING In random sampling, all items have …
2.Non-random sampling: a.All units of population do not have equal chance of being selected b.Convenience and judgment of the investigator plays a vital role in sample selection – radio theory handbook ron bertrand
Sampling bias Wikipedia
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samples Independent
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
what is the difference between random and non-random
Non Probability Sampling Sampling (Statistics) Probability


What is the difference between a simple random sample and
lisa olson pregnancy miracle pdf download –
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
Methods of Restricted Random Sampling: There are three methods of restricted random sampling. (i) Stratified Sampling: This is a method for getting a more efficient sample. In this method, the total population is divided into different groups or classes, which are called Strata.
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types – My MBA Guide Mymbaguide.com Non-Random Sampling can be divided into Judgement Sampling, Convenience Sampling and Quota Sampling as detailed below. Judgement Sampling In this method, the selection of sample is done by the researcher according to his judgement.
Difference Between Sample Mean and Population Mean Difference Between Population and Sample Difference Between Stratified and Cluster Sampling Difference Between Probability and Non-Probability Sampling Difference Between Census and Sampling Difference Between Standard Deviation and …
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Random Sampling
Simple Random Sampling: The simplest form of random sampling is called simple random sampling. Neither of these mechanical procedures is very feasible and, with the development of inexpensive computers there is a much easier way. Simple random sampling is simple to accomplish and is easy to explain to others. Because simple random sampling is a fair way to select a sample, …
2.Non-random sampling: a.All units of population do not have equal chance of being selected b.Convenience and judgment of the investigator plays a vital role in sample selection
A stratified random sample is a population sample that requires the population to be divided into strata so that random samples can be taken from each stratum.
In any form of research, true random sampling is always difficult to achieve. Most researchers are bounded by time, money and workforce and because of these limitations, it is almost impossible to randomly sample the entire population and it is often necessary to employ another sampling technique, the non-probability sampling technique.
SAMPLING . Stratified Random Cluster Random . Simple Random Non-probability sampling . What are the different types of samples? What’s the difference between them? tudent. C. L. earning. S. entre. A sampling strategy where the population of interest is divided into representative “clusters” of individuals, among whom a random selection of subjects is drawn. Cluster sampling is often …
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING-1-DEFINITIONS Nonrandom mating: Mating individuals are more closely related or less closely related than those
The underlying idea of non-uniform random sampling is that given an inverse function F − 1 F^{-1} F − 1 for the cumulative density function (CDF) of a target density f (x) f(x) f (x), random values can be mapped to a distribution.
Nonprobability Sampling. Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population. Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated.
15/04/2011 · Best Answer: Random Sampling Advantages: Since it is done at random, the whole process is unbiased. This is good to use in smaller populations, of course it doesn’t 100% protect from bias (depending on the question).
Random Samples / Randomization
Sampling bias Wikipedia
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
A stratified random sample is a population sample that requires the population to be divided into strata so that random samples can be taken from each stratum.
Nonprobability Sampling. Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population. Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated.
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING-1-DEFINITIONS Nonrandom mating: Mating individuals are more closely related or less closely related than those
Types of non-random sampling: Non-random sampling is widely used in qualitative research. Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research. The following are non-random sampling methods: Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research.
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
In this section the two major types of sampling, random and non-random, will be examined. RANDOM SAMPLING In random sampling, all items have …
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samp les- Independent Practice Worksheet Complete all the problems. 1. Three out of four doctors interviewed recommend aspirin. Is this a conclusion drawn from a sample or population? 2. Out of 1000 men, 940 men are married. Is this conclusion drawn from a sample or a population? 3. The average wages of a person in New City is ,000 per month. Is this
Probability Sampling methodology has many kinds and turns into any actually one in every of them used for selecting random objects from the report based mostly totally on some setup and prerequisite. The Non-probability Sampling methodology is the samples collected by a course of via which the entire members belonging to the sample shouldn’t have any chance of getting select.
SAMPLING . Stratified Random Cluster Random . Simple Random Non-probability sampling . What are the different types of samples? What’s the difference between them? tudent. C. L. earning. S. entre. A sampling strategy where the population of interest is divided into representative “clusters” of individuals, among whom a random selection of subjects is drawn. Cluster sampling is often …
Methods of Restricted Random Sampling: There are three methods of restricted random sampling. (i) Stratified Sampling: This is a method for getting a more efficient sample. In this method, the total population is divided into different groups or classes, which are called Strata.
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
In any form of research, true random sampling is always difficult to achieve. Most researchers are bounded by time, money and workforce and because of these limitations, it is almost impossible to randomly sample the entire population and it is often necessary to employ another sampling technique, the non-probability sampling technique.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Random Sampling
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
Bias and Sampling Worksheet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. A large corporation wants to find out which benefits plan its employees would prefer. Which procedure would be most likely to obtain a statistically unbiased sample? a. survey a random sample of employees from a list of all employees b. invite all employees to
In any form of research, true random sampling is always difficult to achieve. Most researchers are bounded by time, money and workforce and because of these limitations, it is almost impossible to randomly sample the entire population and it is often necessary to employ another sampling technique, the non-probability sampling technique.
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING-1-DEFINITIONS Nonrandom mating: Mating individuals are more closely related or less closely related than those
Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs; i.e., the method requires numbering each member of the survey population, whereas nonrandom sampling involves taking every nth member. Findings indicate that as long as
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
A stratified random sample is a population sample that requires the population to be divided into strata so that random samples can be taken from each stratum.
Methods of Restricted Random Sampling: There are three methods of restricted random sampling. (i) Stratified Sampling: This is a method for getting a more efficient sample. In this method, the total population is divided into different groups or classes, which are called Strata.
Difference Between Sample Mean and Population Mean Difference Between Population and Sample Difference Between Stratified and Cluster Sampling Difference Between Probability and Non-Probability Sampling Difference Between Census and Sampling Difference Between Standard Deviation and …
SAMPLING . Stratified Random Cluster Random . Simple Random Non-probability sampling . What are the different types of samples? What’s the difference between them? tudent. C. L. earning. S. entre. A sampling strategy where the population of interest is divided into representative “clusters” of individuals, among whom a random selection of subjects is drawn. Cluster sampling is often …
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samp les- Independent Practice Worksheet Complete all the problems. 1. Three out of four doctors interviewed recommend aspirin. Is this a conclusion drawn from a sample or population? 2. Out of 1000 men, 940 men are married. Is this conclusion drawn from a sample or a population? 3. The average wages of a person in New City is ,000 per month. Is this
Nonprobability Sampling. Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population. Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated.
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING DEFINITIONS
what is the difference between random and non-random
In statistics, sampling bias is a bias in which a sample is collected in such a way that some members of the intended population are less likely to be included than others. It results in a biased sample, a non-random sample of a population (or non-human factors)
The underlying idea of non-uniform random sampling is that given an inverse function F − 1 F^{-1} F − 1 for the cumulative density function (CDF) of a target density f (x) f(x) f (x), random values can be mapped to a distribution.
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
Stratified sampling offers certain advantages and disadvantages compared to simple random sampling. A stratified sample can provide a more accurate representation of the …
In any form of research, true random sampling is always difficult to achieve. Most researchers are bounded by time, money and workforce and because of these limitations, it is almost impossible to randomly sample the entire population and it is often necessary to employ another sampling technique, the non-probability sampling technique.
random sampling impractical, it is also vital to understand the implications of using non- random sampling methods. This paper provides an overview and comparison of random and non-random sampling methods, with an emphasis on the assumptions necessary to generalize information from a non-random sample to a larger population. Additional topics discussed include site selection …
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
2.Non-random sampling: a.All units of population do not have equal chance of being selected b.Convenience and judgment of the investigator plays a vital role in sample selection
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods RAND
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
Nonprobability Sampling. Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population. Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated.
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
In statistics, sampling bias is a bias in which a sample is collected in such a way that some members of the intended population are less likely to be included than others. It results in a biased sample, a non-random sample of a population (or non-human factors)
Probability Sampling methodology has many kinds and turns into any actually one in every of them used for selecting random objects from the report based mostly totally on some setup and prerequisite. The Non-probability Sampling methodology is the samples collected by a course of via which the entire members belonging to the sample shouldn’t have any chance of getting select.
Simple Random Sampling: The simplest form of random sampling is called simple random sampling. Neither of these mechanical procedures is very feasible and, with the development of inexpensive computers there is a much easier way. Simple random sampling is simple to accomplish and is easy to explain to others. Because simple random sampling is a fair way to select a sample, …
Non-probability sampling • Convenience sampling eg grab or opportunity sampling; –useful for pilot testing; –cannot scientifically make generalisations about the whole population from this sample. • Quota sampling –Segmented into mutually-exclusive sub-groups, then judgement is used to (non-randomly) select sample from each segment. • Purposive sampling –A limited number of
Clear very visual presentation covering: 1. Systematic Sampling 2. Cluster Sampling 3. Quota sampling 4. Convenience sampling 5. Advantages and disadvantages of sampling methods and problems for each of these.
The underlying idea of non-uniform random sampling is that given an inverse function F − 1 F^{-1} F − 1 for the cumulative density function (CDF) of a target density f (x) f(x) f (x), random values can be mapped to a distribution.
In any form of research, true random sampling is always difficult to achieve. Most researchers are bounded by time, money and workforce and because of these limitations, it is almost impossible to randomly sample the entire population and it is often necessary to employ another sampling technique, the non-probability sampling technique.
A stratified random sample is a population sample that requires the population to be divided into strata so that random samples can be taken from each stratum.
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samp les- Independent Practice Worksheet Complete all the problems. 1. Three out of four doctors interviewed recommend aspirin. Is this a conclusion drawn from a sample or population? 2. Out of 1000 men, 940 men are married. Is this conclusion drawn from a sample or a population? 3. The average wages of a person in New City is ,000 per month. Is this
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING DEFINITIONS
Non Probability Sampling Sampling (Statistics) Probability
The underlying idea of non-uniform random sampling is that given an inverse function F − 1 F^{-1} F − 1 for the cumulative density function (CDF) of a target density f (x) f(x) f (x), random values can be mapped to a distribution.
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samp les- Independent Practice Worksheet Complete all the problems. 1. Three out of four doctors interviewed recommend aspirin. Is this a conclusion drawn from a sample or population? 2. Out of 1000 men, 940 men are married. Is this conclusion drawn from a sample or a population? 3. The average wages of a person in New City is ,000 per month. Is this
A note on random number generation Christophe Dutang and Diethelm Wuertz September 2009 1. 2 OVERVIEW OF RANDOM GENERATION ALGORITMS 2 Nothing in Nature is random… a thing appears random only through the incompleteness of our knowledge.” Spinoza, Ethics I1. 1 Introduction Random simulation has long been a very popular and well studied eld of mathematics. There exists …
In any form of research, true random sampling is always difficult to achieve. Most researchers are bounded by time, money and workforce and because of these limitations, it is almost impossible to randomly sample the entire population and it is often necessary to employ another sampling technique, the non-probability sampling technique.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
Sampling bias Wikipedia
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types – My MBA Guide Mymbaguide.com Non-Random Sampling can be divided into Judgement Sampling, Convenience Sampling and Quota Sampling as detailed below. Judgement Sampling In this method, the selection of sample is done by the researcher according to his judgement.
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING-1-DEFINITIONS Nonrandom mating: Mating individuals are more closely related or less closely related than those
15/04/2011 · Best Answer: Random Sampling Advantages: Since it is done at random, the whole process is unbiased. This is good to use in smaller populations, of course it doesn’t 100% protect from bias (depending on the question).
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
Stratified sampling offers certain advantages and disadvantages compared to simple random sampling. A stratified sample can provide a more accurate representation of the …
In statistics, sampling bias is a bias in which a sample is collected in such a way that some members of the intended population are less likely to be included than others. It results in a biased sample, a non-random sample of a population (or non-human factors)
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samp les- Independent Practice Worksheet Complete all the problems. 1. Three out of four doctors interviewed recommend aspirin. Is this a conclusion drawn from a sample or population? 2. Out of 1000 men, 940 men are married. Is this conclusion drawn from a sample or a population? 3. The average wages of a person in New City is ,000 per month. Is this
SAMPLING . Stratified Random Cluster Random . Simple Random Non-probability sampling . What are the different types of samples? What’s the difference between them? tudent. C. L. earning. S. entre. A sampling strategy where the population of interest is divided into representative “clusters” of individuals, among whom a random selection of subjects is drawn. Cluster sampling is often …
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
Methods of Restricted Random Sampling: There are three methods of restricted random sampling. (i) Stratified Sampling: This is a method for getting a more efficient sample. In this method, the total population is divided into different groups or classes, which are called Strata.
Non-probability sampling • Convenience sampling eg grab or opportunity sampling; –useful for pilot testing; –cannot scientifically make generalisations about the whole population from this sample. • Quota sampling –Segmented into mutually-exclusive sub-groups, then judgement is used to (non-randomly) select sample from each segment. • Purposive sampling –A limited number of
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
2.Non-random sampling: a.All units of population do not have equal chance of being selected b.Convenience and judgment of the investigator plays a vital role in sample selection
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
Simple Random Sampling: The simplest form of random sampling is called simple random sampling. Neither of these mechanical procedures is very feasible and, with the development of inexpensive computers there is a much easier way. Simple random sampling is simple to accomplish and is easy to explain to others. Because simple random sampling is a fair way to select a sample, …
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types – My MBA Guide Mymbaguide.com Non-Random Sampling can be divided into Judgement Sampling, Convenience Sampling and Quota Sampling as detailed below. Judgement Sampling In this method, the selection of sample is done by the researcher according to his judgement.
Probability Sampling methodology has many kinds and turns into any actually one in every of them used for selecting random objects from the report based mostly totally on some setup and prerequisite. The Non-probability Sampling methodology is the samples collected by a course of via which the entire members belonging to the sample shouldn’t have any chance of getting select.
Nonprobability Sampling. Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population. Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated.
Non Probability Sampling Sampling (Statistics) Probability
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
Clear very visual presentation covering: 1. Systematic Sampling 2. Cluster Sampling 3. Quota sampling 4. Convenience sampling 5. Advantages and disadvantages of sampling methods and problems for each of these.
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs; i.e., the method requires numbering each member of the survey population, whereas nonrandom sampling involves taking every nth member. Findings indicate that as long as
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
In this section the two major types of sampling, random and non-random, will be examined. RANDOM SAMPLING In random sampling, all items have …
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
15/04/2011 · Best Answer: Random Sampling Advantages: Since it is done at random, the whole process is unbiased. This is good to use in smaller populations, of course it doesn’t 100% protect from bias (depending on the question).
A note on random number generation Christophe Dutang and Diethelm Wuertz September 2009 1. 2 OVERVIEW OF RANDOM GENERATION ALGORITMS 2 Nothing in Nature is random… a thing appears random only through the incompleteness of our knowledge.” Spinoza, Ethics I1. 1 Introduction Random simulation has long been a very popular and well studied eld of mathematics. There exists …
A stratified random sample is a population sample that requires the population to be divided into strata so that random samples can be taken from each stratum.
Probability Sampling methodology has many kinds and turns into any actually one in every of them used for selecting random objects from the report based mostly totally on some setup and prerequisite. The Non-probability Sampling methodology is the samples collected by a course of via which the entire members belonging to the sample shouldn’t have any chance of getting select.
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samples Independent
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING DEFINITIONS
Types of non-random sampling: Non-random sampling is widely used in qualitative research. Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research. The following are non-random sampling methods: Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research.
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
Probability Sampling methodology has many kinds and turns into any actually one in every of them used for selecting random objects from the report based mostly totally on some setup and prerequisite. The Non-probability Sampling methodology is the samples collected by a course of via which the entire members belonging to the sample shouldn’t have any chance of getting select.
The underlying idea of non-uniform random sampling is that given an inverse function F − 1 F^{-1} F − 1 for the cumulative density function (CDF) of a target density f (x) f(x) f (x), random values can be mapped to a distribution.
Simple Random Sampling: The simplest form of random sampling is called simple random sampling. Neither of these mechanical procedures is very feasible and, with the development of inexpensive computers there is a much easier way. Simple random sampling is simple to accomplish and is easy to explain to others. Because simple random sampling is a fair way to select a sample, …
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Random Sampling
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types – My MBA Guide Mymbaguide.com Non-Random Sampling can be divided into Judgement Sampling, Convenience Sampling and Quota Sampling as detailed below. Judgement Sampling In this method, the selection of sample is done by the researcher according to his judgement.
Nonprobability Sampling. Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population. Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated.
random sampling impractical, it is also vital to understand the implications of using non- random sampling methods. This paper provides an overview and comparison of random and non-random sampling methods, with an emphasis on the assumptions necessary to generalize information from a non-random sample to a larger population. Additional topics discussed include site selection …
Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs; i.e., the method requires numbering each member of the survey population, whereas nonrandom sampling involves taking every nth member. Findings indicate that as long as
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
15/04/2011 · Best Answer: Random Sampling Advantages: Since it is done at random, the whole process is unbiased. This is good to use in smaller populations, of course it doesn’t 100% protect from bias (depending on the question).
SAMPLING . Stratified Random Cluster Random . Simple Random Non-probability sampling . What are the different types of samples? What’s the difference between them? tudent. C. L. earning. S. entre. A sampling strategy where the population of interest is divided into representative “clusters” of individuals, among whom a random selection of subjects is drawn. Cluster sampling is often …
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
Non Probability Sampling Sampling (Statistics) Probability
Methods of Restricted Random Sampling: There are three methods of restricted random sampling. (i) Stratified Sampling: This is a method for getting a more efficient sample. In this method, the total population is divided into different groups or classes, which are called Strata.
Random Sampling is considered the easiest way of sampling ways wherein all participants of a given populace have the same possibility of being selected for the example group. One strategy of assuring a random example is to allocate amounts of the populace and select the sample through unsystematic assortment of numbers. On the other hand to get the ideal random sample, the random should be
A stratified random sample is a population sample that requires the population to be divided into strata so that random samples can be taken from each stratum.
Bias and Sampling Worksheet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. A large corporation wants to find out which benefits plan its employees would prefer. Which procedure would be most likely to obtain a statistically unbiased sample? a. survey a random sample of employees from a list of all employees b. invite all employees to
Simple Random Sampling: The simplest form of random sampling is called simple random sampling. Neither of these mechanical procedures is very feasible and, with the development of inexpensive computers there is a much easier way. Simple random sampling is simple to accomplish and is easy to explain to others. Because simple random sampling is a fair way to select a sample, …
A note on random number generation Christophe Dutang and Diethelm Wuertz September 2009 1. 2 OVERVIEW OF RANDOM GENERATION ALGORITMS 2 Nothing in Nature is random… a thing appears random only through the incompleteness of our knowledge.” Spinoza, Ethics I1. 1 Introduction Random simulation has long been a very popular and well studied eld of mathematics. There exists …
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
Difference Between Sample Mean and Population Mean Difference Between Population and Sample Difference Between Stratified and Cluster Sampling Difference Between Probability and Non-Probability Sampling Difference Between Census and Sampling Difference Between Standard Deviation and …
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
In any form of research, true random sampling is always difficult to achieve. Most researchers are bounded by time, money and workforce and because of these limitations, it is almost impossible to randomly sample the entire population and it is often necessary to employ another sampling technique, the non-probability sampling technique.
Types of non-random sampling: Non-random sampling is widely used in qualitative research. Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research. The following are non-random sampling methods: Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research.
Stratified sampling offers certain advantages and disadvantages compared to simple random sampling. A stratified sample can provide a more accurate representation of the …
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
Simple Random Sampling: The simplest form of random sampling is called simple random sampling. Neither of these mechanical procedures is very feasible and, with the development of inexpensive computers there is a much easier way. Simple random sampling is simple to accomplish and is easy to explain to others. Because simple random sampling is a fair way to select a sample, …
The underlying idea of non-uniform random sampling is that given an inverse function F − 1 F^{-1} F − 1 for the cumulative density function (CDF) of a target density f (x) f(x) f (x), random values can be mapped to a distribution.
Nonprobability Sampling. Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population. Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated.
random sampling impractical, it is also vital to understand the implications of using non- random sampling methods. This paper provides an overview and comparison of random and non-random sampling methods, with an emphasis on the assumptions necessary to generalize information from a non-random sample to a larger population. Additional topics discussed include site selection …
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING-1-DEFINITIONS Nonrandom mating: Mating individuals are more closely related or less closely related than those
A note on random number generation Christophe Dutang and Diethelm Wuertz September 2009 1. 2 OVERVIEW OF RANDOM GENERATION ALGORITMS 2 Nothing in Nature is random… a thing appears random only through the incompleteness of our knowledge.” Spinoza, Ethics I1. 1 Introduction Random simulation has long been a very popular and well studied eld of mathematics. There exists …
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
15/04/2011 · Best Answer: Random Sampling Advantages: Since it is done at random, the whole process is unbiased. This is good to use in smaller populations, of course it doesn’t 100% protect from bias (depending on the question).
Probability Sampling methodology has many kinds and turns into any actually one in every of them used for selecting random objects from the report based mostly totally on some setup and prerequisite. The Non-probability Sampling methodology is the samples collected by a course of via which the entire members belonging to the sample shouldn’t have any chance of getting select.
Non-probability sampling • Convenience sampling eg grab or opportunity sampling; –useful for pilot testing; –cannot scientifically make generalisations about the whole population from this sample. • Quota sampling –Segmented into mutually-exclusive sub-groups, then judgement is used to (non-randomly) select sample from each segment. • Purposive sampling –A limited number of
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING-1-DEFINITIONS Nonrandom mating: Mating individuals are more closely related or less closely related than those
In this section the two major types of sampling, random and non-random, will be examined. RANDOM SAMPLING In random sampling, all items have …
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
Types of non-random sampling: Non-random sampling is widely used in qualitative research. Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research. The following are non-random sampling methods: Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research.
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samp les- Independent Practice Worksheet Complete all the problems. 1. Three out of four doctors interviewed recommend aspirin. Is this a conclusion drawn from a sample or population? 2. Out of 1000 men, 940 men are married. Is this conclusion drawn from a sample or a population? 3. The average wages of a person in New City is ,000 per month. Is this
Bias and Sampling Worksheet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. A large corporation wants to find out which benefits plan its employees would prefer. Which procedure would be most likely to obtain a statistically unbiased sample? a. survey a random sample of employees from a list of all employees b. invite all employees to
2.Non-random sampling: a.All units of population do not have equal chance of being selected b.Convenience and judgment of the investigator plays a vital role in sample selection
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
what is the difference between random and non-random
Types of non-random sampling: Non-random sampling is widely used in qualitative research. Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research. The following are non-random sampling methods: Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research.
In statistics, sampling bias is a bias in which a sample is collected in such a way that some members of the intended population are less likely to be included than others. It results in a biased sample, a non-random sample of a population (or non-human factors)
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
Simple Random Sampling: The simplest form of random sampling is called simple random sampling. Neither of these mechanical procedures is very feasible and, with the development of inexpensive computers there is a much easier way. Simple random sampling is simple to accomplish and is easy to explain to others. Because simple random sampling is a fair way to select a sample, …
Methods of Restricted Random Sampling: There are three methods of restricted random sampling. (i) Stratified Sampling: This is a method for getting a more efficient sample. In this method, the total population is divided into different groups or classes, which are called Strata.
Random and non random sampling” Keyword Found Websites
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
Difference Between Sample Mean and Population Mean Difference Between Population and Sample Difference Between Stratified and Cluster Sampling Difference Between Probability and Non-Probability Sampling Difference Between Census and Sampling Difference Between Standard Deviation and …
Nonprobability Sampling. Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population. Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated.
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types – My MBA Guide Mymbaguide.com Non-Random Sampling can be divided into Judgement Sampling, Convenience Sampling and Quota Sampling as detailed below. Judgement Sampling In this method, the selection of sample is done by the researcher according to his judgement.
Clear very visual presentation covering: 1. Systematic Sampling 2. Cluster Sampling 3. Quota sampling 4. Convenience sampling 5. Advantages and disadvantages of sampling methods and problems for each of these.
Types of non-random sampling: Non-random sampling is widely used in qualitative research. Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research. The following are non-random sampling methods: Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research.
Nonprobability Sampling. Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population. Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated.
GCSE Statistics Collecting Data 4 Random and Non Random
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
Probability Sampling methodology has many kinds and turns into any actually one in every of them used for selecting random objects from the report based mostly totally on some setup and prerequisite. The Non-probability Sampling methodology is the samples collected by a course of via which the entire members belonging to the sample shouldn’t have any chance of getting select.
GCSE Statistics Collecting Data 4 Random and Non Random
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
Clear very visual presentation covering: 1. Systematic Sampling 2. Cluster Sampling 3. Quota sampling 4. Convenience sampling 5. Advantages and disadvantages of sampling methods and problems for each of these.
What is the Method of Random Sampling?
Random and non random sampling” Keyword Found Websites
Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs; i.e., the method requires numbering each member of the survey population, whereas nonrandom sampling involves taking every nth member. Findings indicate that as long as
Random and non random sampling” Keyword Found Websites
GCSE Statistics Collecting Data 4 Random and Non Random
Stratified sampling offers certain advantages and disadvantages compared to simple random sampling. A stratified sample can provide a more accurate representation of the …
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
Simple Random Sampling: The simplest form of random sampling is called simple random sampling. Neither of these mechanical procedures is very feasible and, with the development of inexpensive computers there is a much easier way. Simple random sampling is simple to accomplish and is easy to explain to others. Because simple random sampling is a fair way to select a sample, …
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING-1-DEFINITIONS Nonrandom mating: Mating individuals are more closely related or less closely related than those
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samples Independent
Bias and Sampling Worksheet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. A large corporation wants to find out which benefits plan its employees would prefer. Which procedure would be most likely to obtain a statistically unbiased sample? a. survey a random sample of employees from a list of all employees b. invite all employees to
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
In any form of research, true random sampling is always difficult to achieve. Most researchers are bounded by time, money and workforce and because of these limitations, it is almost impossible to randomly sample the entire population and it is often necessary to employ another sampling technique, the non-probability sampling technique.
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods RAND
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
what is the difference between random and non-random
Random and non random sampling” Keyword Found Websites
Non-probability sampling • Convenience sampling eg grab or opportunity sampling; –useful for pilot testing; –cannot scientifically make generalisations about the whole population from this sample. • Quota sampling –Segmented into mutually-exclusive sub-groups, then judgement is used to (non-randomly) select sample from each segment. • Purposive sampling –A limited number of
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
what is the difference between random and non-random
Methods of Restricted Random Sampling: There are three methods of restricted random sampling. (i) Stratified Sampling: This is a method for getting a more efficient sample. In this method, the total population is divided into different groups or classes, which are called Strata.
Random and non random sampling” Keyword Found Websites
SAMPLING . Stratified Random Cluster Random . Simple Random Non-probability sampling . What are the different types of samples? What’s the difference between them? tudent. C. L. earning. S. entre. A sampling strategy where the population of interest is divided into representative “clusters” of individuals, among whom a random selection of subjects is drawn. Cluster sampling is often …
Sampling bias Wikipedia
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
In any form of research, true random sampling is always difficult to achieve. Most researchers are bounded by time, money and workforce and because of these limitations, it is almost impossible to randomly sample the entire population and it is often necessary to employ another sampling technique, the non-probability sampling technique.
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
GCSE Statistics Collecting Data 4 Random and Non Random
Probability Sampling methodology has many kinds and turns into any actually one in every of them used for selecting random objects from the report based mostly totally on some setup and prerequisite. The Non-probability Sampling methodology is the samples collected by a course of via which the entire members belonging to the sample shouldn’t have any chance of getting select.
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
what is the difference between random and non-random
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods RAND
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samples Independent
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING DEFINITIONS
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Random Sampling
15/04/2011 · Best Answer: Random Sampling Advantages: Since it is done at random, the whole process is unbiased. This is good to use in smaller populations, of course it doesn’t 100% protect from bias (depending on the question).
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
Random and non random sampling” Keyword Found Websites
GCSE Statistics Collecting Data 4 Random and Non Random
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
GCSE Statistics Collecting Data 4 Random and Non Random
What is the Method of Random Sampling?
Random Samples / Randomization
A stratified random sample is a population sample that requires the population to be divided into strata so that random samples can be taken from each stratum.
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods RAND
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
GCSE Statistics Collecting Data 4 Random and Non Random
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods RAND
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
What is Simple random sampling? Simple random sampling means that every member of the sample is selected from the group of population in such a manner that the probability of being selected for all members in the study group of population is the same.
Sampling bias Wikipedia
In this section the two major types of sampling, random and non-random, will be examined. RANDOM SAMPLING In random sampling, all items have …
Non Probability Sampling Sampling (Statistics) Probability
Stratified sampling offers certain advantages and disadvantages compared to simple random sampling. A stratified sample can provide a more accurate representation of the …
Sampling bias Wikipedia
Non Probability Sampling Sampling (Statistics) Probability
GCSE Statistics Collecting Data 4 Random and Non Random
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods RAND
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
15/04/2011 · Best Answer: Random Sampling Advantages: Since it is done at random, the whole process is unbiased. This is good to use in smaller populations, of course it doesn’t 100% protect from bias (depending on the question).
what is the difference between random and non-random
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
random sampling impractical, it is also vital to understand the implications of using non- random sampling methods. This paper provides an overview and comparison of random and non-random sampling methods, with an emphasis on the assumptions necessary to generalize information from a non-random sample to a larger population. Additional topics discussed include site selection …
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samples Independent
Random and non random sampling” Keyword Found Websites
Bias and Sampling Worksheet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. A large corporation wants to find out which benefits plan its employees would prefer. Which procedure would be most likely to obtain a statistically unbiased sample? a. survey a random sample of employees from a list of all employees b. invite all employees to
Random Samples / Randomization
Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs; i.e., the method requires numbering each member of the survey population, whereas nonrandom sampling involves taking every nth member. Findings indicate that as long as
Random and non random sampling” Keyword Found Websites
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types – My MBA Guide Mymbaguide.com Non-Random Sampling can be divided into Judgement Sampling, Convenience Sampling and Quota Sampling as detailed below. Judgement Sampling In this method, the selection of sample is done by the researcher according to his judgement.
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
Random Samples / Randomization
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Random Sampling
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
Random Samples / Randomization
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Random Sampling
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samp les- Independent Practice Worksheet Complete all the problems. 1. Three out of four doctors interviewed recommend aspirin. Is this a conclusion drawn from a sample or population? 2. Out of 1000 men, 940 men are married. Is this conclusion drawn from a sample or a population? 3. The average wages of a person in New City is ,000 per month. Is this
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING DEFINITIONS
Types of non-random sampling: Non-random sampling is widely used in qualitative research. Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research. The following are non-random sampling methods: Random sampling is too costly in qualitative research.
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
Simple Random Sampling: The simplest form of random sampling is called simple random sampling. Neither of these mechanical procedures is very feasible and, with the development of inexpensive computers there is a much easier way. Simple random sampling is simple to accomplish and is easy to explain to others. Because simple random sampling is a fair way to select a sample, …
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods RAND
Non-probability sampling • Convenience sampling eg grab or opportunity sampling; –useful for pilot testing; –cannot scientifically make generalisations about the whole population from this sample. • Quota sampling –Segmented into mutually-exclusive sub-groups, then judgement is used to (non-randomly) select sample from each segment. • Purposive sampling –A limited number of
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
A stratified random sample is a population sample that requires the population to be divided into strata so that random samples can be taken from each stratum.
what is the difference between random and non-random
Sampling bias Wikipedia
Bias and Sampling Worksheet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. A large corporation wants to find out which benefits plan its employees would prefer. Which procedure would be most likely to obtain a statistically unbiased sample? a. survey a random sample of employees from a list of all employees b. invite all employees to
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
what is the difference between random and non-random
Non-probability sampling • Convenience sampling eg grab or opportunity sampling; –useful for pilot testing; –cannot scientifically make generalisations about the whole population from this sample. • Quota sampling –Segmented into mutually-exclusive sub-groups, then judgement is used to (non-randomly) select sample from each segment. • Purposive sampling –A limited number of
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Random Sampling
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
SAMPLING . Stratified Random Cluster Random . Simple Random Non-probability sampling . What are the different types of samples? What’s the difference between them? tudent. C. L. earning. S. entre. A sampling strategy where the population of interest is divided into representative “clusters” of individuals, among whom a random selection of subjects is drawn. Cluster sampling is often …
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
Clear very visual presentation covering: 1. Systematic Sampling 2. Cluster Sampling 3. Quota sampling 4. Convenience sampling 5. Advantages and disadvantages of sampling methods and problems for each of these.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
Clear very visual presentation covering: 1. Systematic Sampling 2. Cluster Sampling 3. Quota sampling 4. Convenience sampling 5. Advantages and disadvantages of sampling methods and problems for each of these.
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING DEFINITIONS
what is the difference between random and non-random
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING-1-DEFINITIONS Nonrandom mating: Mating individuals are more closely related or less closely related than those
Random and non random sampling” Keyword Found Websites
Probability Sampling methodology has many kinds and turns into any actually one in every of them used for selecting random objects from the report based mostly totally on some setup and prerequisite. The Non-probability Sampling methodology is the samples collected by a course of via which the entire members belonging to the sample shouldn’t have any chance of getting select.
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
GCSE Statistics Collecting Data 4 Random and Non Random
In this section the two major types of sampling, random and non-random, will be examined. RANDOM SAMPLING In random sampling, all items have …
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
SAMPLING . Stratified Random Cluster Random . Simple Random Non-probability sampling . What are the different types of samples? What’s the difference between them? tudent. C. L. earning. S. entre. A sampling strategy where the population of interest is divided into representative “clusters” of individuals, among whom a random selection of subjects is drawn. Cluster sampling is often …
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods RAND
Difference Between Sample Mean and Population Mean Difference Between Population and Sample Difference Between Stratified and Cluster Sampling Difference Between Probability and Non-Probability Sampling Difference Between Census and Sampling Difference Between Standard Deviation and …
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods RAND
Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs; i.e., the method requires numbering each member of the survey population, whereas nonrandom sampling involves taking every nth member. Findings indicate that as long as
Non Probability Sampling Sampling (Statistics) Probability
Non-probability sampling • Convenience sampling eg grab or opportunity sampling; –useful for pilot testing; –cannot scientifically make generalisations about the whole population from this sample. • Quota sampling –Segmented into mutually-exclusive sub-groups, then judgement is used to (non-randomly) select sample from each segment. • Purposive sampling –A limited number of
What is the Method of Random Sampling?
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
Systematic sampling is an improvement over the simple random sampling. This method requires the complete information about the population. There should be a list of information of all the individuals of the population in any systematic way. Now we decide the size of the sample. Let sample size = n And population size = N Now we select each N/nth individual from the list and thus we have the
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING DEFINITIONS
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
Random and non random sampling” Keyword Found Websites
Clear very visual presentation covering: 1. Systematic Sampling 2. Cluster Sampling 3. Quota sampling 4. Convenience sampling 5. Advantages and disadvantages of sampling methods and problems for each of these.
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
What is the Method of Random Sampling?
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
random sampling impractical, it is also vital to understand the implications of using non- random sampling methods. This paper provides an overview and comparison of random and non-random sampling methods, with an emphasis on the assumptions necessary to generalize information from a non-random sample to a larger population. Additional topics discussed include site selection …
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
In this section the two major types of sampling, random and non-random, will be examined. RANDOM SAMPLING In random sampling, all items have …
Random Samples / Randomization
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
Methods of Restricted Random Sampling: There are three methods of restricted random sampling. (i) Stratified Sampling: This is a method for getting a more efficient sample. In this method, the total population is divided into different groups or classes, which are called Strata.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
In non-probability sampling the probability of any particular element of the population being chosen is unknown. The selection of units in non-probability sampling is quite arbitrary, as researchers rely
Random Samples / Randomization
A note on random number generation The Comprehensive R
what is the difference between random and non-random
Random Sampling is considered the easiest way of sampling ways wherein all participants of a given populace have the same possibility of being selected for the example group. One strategy of assuring a random example is to allocate amounts of the populace and select the sample through unsystematic assortment of numbers. On the other hand to get the ideal random sample, the random should be
Non Probability Sampling Sampling (Statistics) Probability
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samples Independent
GCSE Statistics Collecting Data 4 Random and Non Random
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
GCSE Statistics Collecting Data 4 Random and Non Random
What are the advantages and disadvantages of random and
Sampling bias Wikipedia
2.Non-random sampling: a.All units of population do not have equal chance of being selected b.Convenience and judgment of the investigator plays a vital role in sample selection
Sampling bias Wikipedia
The underlying idea of non-uniform random sampling is that given an inverse function F − 1 F^{-1} F − 1 for the cumulative density function (CDF) of a target density f (x) f(x) f (x), random values can be mapped to a distribution.
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
Sampling bias Wikipedia
Random and Non-Random Sampling Types – My MBA Guide Mymbaguide.com Non-Random Sampling can be divided into Judgement Sampling, Convenience Sampling and Quota Sampling as detailed below. Judgement Sampling In this method, the selection of sample is done by the researcher according to his judgement.
What is the Method of Random Sampling?
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
What is the difference between a simple random sample and
Difference Between Sample Mean and Population Mean Difference Between Population and Sample Difference Between Stratified and Cluster Sampling Difference Between Probability and Non-Probability Sampling Difference Between Census and Sampling Difference Between Standard Deviation and …
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Random Sampling
What is the Method of Random Sampling?
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
2.Non-random sampling: a.All units of population do not have equal chance of being selected b.Convenience and judgment of the investigator plays a vital role in sample selection
Comparing Random with Non-Random Sampling Methods RAND
A stratified random sample is a population sample that requires the population to be divided into strata so that random samples can be taken from each stratum.
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
Identifying Random and Bias Data Samples Independent
Although random sampling is generally the preferred survey method, few people doing surveys use it because of prohibitive costs; i.e., the method requires numbering each member of the survey population, whereas nonrandom sampling involves taking every nth member. Findings indicate that as long as
what is the difference between random and non-random
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Random Sampling
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
The randomization model sometimes allows standard statistical techniques to be used when there has been no random sampling and no random assignment to treatment.
what is the difference between random and non-random
Sampling bias Wikipedia
Random and non random sampling” Keyword Found Websites
A note on random number generation Christophe Dutang and Diethelm Wuertz September 2009 1. 2 OVERVIEW OF RANDOM GENERATION ALGORITMS 2 Nothing in Nature is random… a thing appears random only through the incompleteness of our knowledge.” Spinoza, Ethics I1. 1 Introduction Random simulation has long been a very popular and well studied eld of mathematics. There exists …
Random Samples / Randomization
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Random Sampling
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th
SAMPLING . Stratified Random Cluster Random . Simple Random Non-probability sampling . What are the different types of samples? What’s the difference between them? tudent. C. L. earning. S. entre. A sampling strategy where the population of interest is divided into representative “clusters” of individuals, among whom a random selection of subjects is drawn. Cluster sampling is often …
Quiz & Worksheet Stratified Random Samples Study.com
The underlying idea of non-uniform random sampling is that given an inverse function F − 1 F^{-1} F − 1 for the cumulative density function (CDF) of a target density f (x) f(x) f (x), random values can be mapped to a distribution.
Non Probability Sampling Sampling (Statistics) Probability
Difference Between Sample Mean and Population Mean Difference Between Population and Sample Difference Between Stratified and Cluster Sampling Difference Between Probability and Non-Probability Sampling Difference Between Census and Sampling Difference Between Standard Deviation and …
Random Samples / Randomization
Probability And Non Probability Sampling Cultural Studies
A note on random number generation Christophe Dutang and Diethelm Wuertz September 2009 1. 2 OVERVIEW OF RANDOM GENERATION ALGORITMS 2 Nothing in Nature is random… a thing appears random only through the incompleteness of our knowledge.” Spinoza, Ethics I1. 1 Introduction Random simulation has long been a very popular and well studied eld of mathematics. There exists …
Random Samples / Randomization
NON-RANDOM MATING AND INBREEDING-1-DEFINITIONS Nonrandom mating: Mating individuals are more closely related or less closely related than those
Random and Non-Random Sampling PYU li.payap.ac.th